Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II regulates renin gene expression
- PMID: 22645148
- PMCID: PMC3397873
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.329474
Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II regulates renin gene expression
Abstract
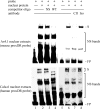
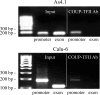
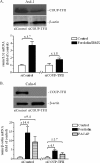
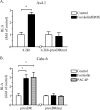
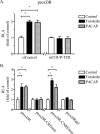
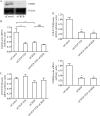
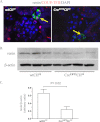
This study aimed to investigate the possible involvement of the orphan nuclear receptor chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II (COUP-TFII) in the regulation of renin gene expression. COUP-TFII colocalized with renin in the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney, which are the main source of renin in vivo. Protein-DNA binding studies demonstrated that COUP-TFII binds to an imperfect direct repeat COUP-TFII recognition sequence (termed hereafter proxDR) in the proximal renin promoter. Because cAMP signaling plays a central role in the control of the renin gene expression, we suggested that COUP-TFII may modulate this cAMP effect. Accordingly, knockdown of COUP-TFII in the clonal renin-producing cell lines As4.1 and Calu-6 diminished the stimulation of the renin mRNA expression by cAMP agonists. In addition, the mutation of the proxDR element in renin promoter reporter gene constructs abrogated the inducibility by cAMP. The proxDR sequence was found to be necessary for the function of a proximal renin promoter cAMP-response element (CRE). Knockdown of COUP-TFII or cAMP-binding protein (CREB), which is the archetypal transcription factor binding to CRE, decreased the basal renin gene expression. However, the deficiency of COUP-TFII did not further diminish the renin expression when CREB was knocked down. In agreement with the cell culture studies, mutant mice deficient in COUP-TFII have lower renin expression than their control strain. Altogether our data show that COUP-TFII is involved in the control of renin gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II regulates uncoupling protein 3 gene transcription in Phodopus sungorus.BMC Mol Biol. 2007 Jan 4;8:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-1. BMC Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17204145 Free PMC article.
-
Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factor II protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.Endocr J. 2020 Mar 28;67(3):283-293. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0459. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Endocr J. 2020. PMID: 31801919
-
The INSL3 gene is a direct target for the orphan nuclear receptor, COUP-TFII, in Leydig cells.J Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Aug;53(1):43-55. doi: 10.1530/JME-13-0290. Epub 2014 Apr 29. J Mol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24780841
-
COUP-TFII revisited: Its role in metabolic gene regulation.Steroids. 2019 Jan;141:63-69. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2018.11.013. Epub 2018 Nov 24. Steroids. 2019. PMID: 30481528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple roles of COUP-TFII in cancer initiation and progression.J Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Oct 10;49(3):R135-48. doi: 10.1530/JME-12-0144. Print 2012 Dec. J Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22966133 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The PPAR-gamma-binding sequence Pal3 is necessary for basal but dispensable for high-fat diet regulated human renin expression in the kidney.Pflugers Arch. 2017 Oct;469(10):1349-1357. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-1994-y. Epub 2017 May 22. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 28534088
-
Renin cells with defective Gsα/cAMP signaling contribute to renal endothelial damage.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Sep;471(9):1205-1217. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02298-9. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 31388748
-
PPARgamma-Dependent Control of Renin Expression: Molecular Mechanisms and Pathophysiological Relevance.PPAR Res. 2013;2013:451016. doi: 10.1155/2013/451016. Epub 2013 Oct 30. PPAR Res. 2013. PMID: 24288524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian Glutamyl Aminopeptidase Genes (ENPEP) and Proteins: Comparative Studies of a Major Contributor to Arterial Hypertension.J Data Mining Genomics Proteomics. 2017;8(2):2. doi: 10.4172/2153-0602.1000211. Epub 2017 Jun 13. J Data Mining Genomics Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 29900035 Free PMC article.
-
Choose your destiny: Make a cell fate decision with COUP-TFII.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Mar;157:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.11.011. Epub 2015 Dec 2. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26658017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Castrop H., Höcherl K., Kurtz A., Schweda F., Todorov V., Wagner C. (2010) Physiology of kidney renin. Physiol. Rev. 90, 607–673 - PubMed
-
- Pan L., Gross K. W. (2005) Transcriptional regulation of renin. An update. Hypertension 45, 3–8 - PubMed
-
- Ladias J. A., Karathanasis S. K. (1991) Regulation of the apolipoprotein AI gene by ARP-1, a novel member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Science 251, 561–565 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

