The iPlant Collaborative: Cyberinfrastructure for Plant Biology
- PMID: 22645531
- PMCID: PMC3355756
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2011.00034
The iPlant Collaborative: Cyberinfrastructure for Plant Biology
Abstract
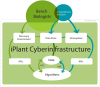
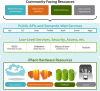
The iPlant Collaborative (iPlant) is a United States National Science Foundation (NSF) funded project that aims to create an innovative, comprehensive, and foundational cyberinfrastructure in support of plant biology research (PSCIC, 2006). iPlant is developing cyberinfrastructure that uniquely enables scientists throughout the diverse fields that comprise plant biology to address Grand Challenges in new ways, to stimulate and facilitate cross-disciplinary research, to promote biology and computer science research interactions, and to train the next generation of scientists on the use of cyberinfrastructure in research and education. Meeting humanity's projected demands for agricultural and forest products and the expectation that natural ecosystems be managed sustainably will require synergies from the application of information technologies. The iPlant cyberinfrastructure design is based on an unprecedented period of research community input, and leverages developments in high-performance computing, data storage, and cyberinfrastructure for the physical sciences. iPlant is an open-source project with application programming interfaces that allow the community to extend the infrastructure to meet its needs. iPlant is sponsoring community-driven workshops addressing specific scientific questions via analysis tool integration and hypothesis testing. These workshops teach researchers how to add bioinformatics tools and/or datasets into the iPlant cyberinfrastructure enabling plant scientists to perform complex analyses on large datasets without the need to master the command-line or high-performance computational services.
Keywords: bioinformatics; computational biology; cyberinfrastructure; plant biology.
Figures

References
-
- Altintas I., Berkley C., Jaeger E., Jones M., Ludascher B., Mock S. (2004). “Kepler: an extensible system for design and execution of scientific workflows,” in 16th International Conference on Scientific and Statistical Database Management, Santorini Island
-
- Atkins D. E., Droegemeier K. K., Feldman H., Garcia-Molina H., Klein M. L., Messerschmitt D. G., Messina P., Ostriker J. P., Wright M. H. (2003). Revolutionizing Science and Engineering Through Cyberinfrastructure. Report of the national science foundation blue-ribbon advisory panel on cyberinfrastructure. Arlington, VA: Office of Cyberinfrastructure, The National Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

