Association of rs2072183 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations
- PMID: 22646906
- PMCID: PMC3422998
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-61
Association of rs2072183 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations
Abstract
Background: Niemann-pick C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) is a key protein for intestinal cholesterol transportation. Common single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the NPC1L1 gene have been associated with cholesterol absorption and serum lipid levels. The present study was undertaken to explore the possible association of NPC1L1 rs2072183 1735 C > G SNP and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.
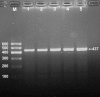
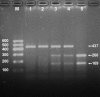
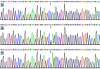
Methods: Genotyping of the rs2072183 SNP was performed in 688 subjects of Mulao and 738 participants of Han Chinese. The interactions between NPC1L1 1735 C > G polymorphism and several environmental factors on serum lipid phenotypes were tested using the factorial design covariance analysis after controlling for potential confounders.
Results: The frequency of G allele was lower in Mulao than in Han (29.72% vs. 37.26%, P < 0.001). The frequency of CC, CG and GG genotypes was 49.85%, 40.84% and 9.31% in Mulao, and 39.30%, 46.88% and 13.82% in Han (P < 0.001); respectively. The levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), apolipoprotein (Apo) B and the ratio of ApoAI/ApoB in Han but not in Mulao were different among the three genotypes (P < 0.05 for all), the subjects with GG and CG genotypes had higher LDL-C, ApoB levels and lower ApoAI/ApoB ratio than the subjects with CC genotype. Subgroup analysis showed that the G allele carriers in Han had higher total cholesterol (TC), LDL-C and ApoB levels in males (P < 0.05) and lower ApoAI/ApoB ratio in both sexes (P < 0.05) than the G allele noncarriers. The G allele carriers in Mulao had higher TC and LDL-C levels in males (P < 0.05) and lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels in both sexes (P < 0.05) than the G allele noncarriers. Serum TC, LDL-C, ApoB levels and ApoAI/ApoB ratio were correlated with genotypes in Han males (P < 0.05) but not in females. Serum lipid parameters were also correlated with several environmental factors. The genotypes of rs2072183 SNP were interacted with gender or cigarette smoking to influence serum TC and HDL-C levels in Mulao, whereas the genotypes of rs2072183 SNP were interacted with several environmental factors to influence all seven lipid traits in Han (P < 0.05-0.01).
Conclusions: The present study suggests that the rs2072183 SNP in NPC1L1 gene and its association with serum lipid profiles are different between the Mulao and Han populations. The difference in serum lipid profiles between the two ethnic groups might partly result from different rs2072183 SNP or NPC1L1 gene-environmental interactions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of the rs7395662 SNP in the MADD-FOLH1 and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Int J Med Sci. 2013 Sep 1;10(11):1537-46. doi: 10.7150/ijms.6421. eCollection 2013. Int J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24046529 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific association of rs16996148 SNP in the NCAN/CILP2/PBX4 and serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Dec 31;10:248. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-248. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22208664 Free PMC article.
-
The SCARB1 rs5888 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Mulao and Han populations.Int J Med Sci. 2012;9(8):715-24. doi: 10.7150/ijms.4815. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Int J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 23091409 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the TRIB1 tribbles homolog 1 gene rs17321515 A>G polymorphism and serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Dec 6;10:230. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-230. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22145581 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the GALNT2 gene polymorphisms and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Sep 20;10:160. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-160. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 21933382 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Novel gene-by-environment interactions: APOB and NPC1L1 variants affect the relationship between dietary and total plasma cholesterol.J Lipid Res. 2013 May;54(5):1512-20. doi: 10.1194/jlr.P035238. Epub 2013 Mar 11. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23482652 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the MLXIPL/TBL2 rs17145738 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Mulao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2013 Oct 25;12:156. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-156. Lipids Health Dis. 2013. PMID: 24160749 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of ezetimibe is not related to NPC1L1 gene polymorphisms in a pilot study of Chilean hypercholesterolemic subjects.Mol Diagn Ther. 2015 Feb;19(1):45-52. doi: 10.1007/s40291-014-0128-x. Mol Diagn Ther. 2015. PMID: 25589339
-
The NPC1L1 Polymorphism 1679C>G Is Associated with Gallstone Disease in Chinese Patients.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 22;11(1):e0147562. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147562. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26800364 Free PMC article.
-
CYP7A1, NPC1L1, ABCB1, and CD36 Polymorphisms Are Associated with Increased Serum Coenzyme Q10 after Long-Term Supplementation in Women.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 11;10(3):431. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030431. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33799730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Long-Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischaemic Disease (LIPID) Study Group. Prevention of cardiovascular events and death with pravastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and a broad range of initial cholesterol levels. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1349–1357. - PubMed
-
- Horiuchi H, Kita T, Mabuchi H, Matsuzaki M, Matsuzawa Y, Nakaya N, Oikawa S, Saito Y, Sasaki J, Shimamoto K, Itakura H. J-LIT Study Group. Primary cardiovascular events and serum lipid levels in elderly Japanese with hypercholesterolemia undergoing 6-year simvastatin treatment: a subanalysis of the Japan lipid intervention trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52:1981–1987. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52552.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

