AlzPathway: a comprehensive map of signaling pathways of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22647208
- PMCID: PMC3411424
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-52
AlzPathway: a comprehensive map of signaling pathways of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia among the elderly. To clarify pathogenesis of AD, thousands of reports have been accumulating. However, knowledge of signaling pathways in the field of AD has not been compiled as a database before.
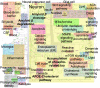
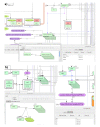
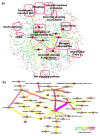
Description: Here, we have constructed a publicly available pathway map called "AlzPathway" that comprehensively catalogs signaling pathways in the field of AD. We have collected and manually curated over 100 review articles related to AD, and have built an AD pathway map using CellDesigner. AlzPathway is currently composed of 1347 molecules and 1070 reactions in neuron, brain blood barrier, presynaptic, postsynaptic, astrocyte, and microglial cells and their cellular localizations. AlzPathway is available as both the SBML (Systems Biology Markup Language) map for CellDesigner and the high resolution image map. AlzPathway is also available as a web service (online map) based on Payao system, a community-based, collaborative web service platform for pathway model curation, enabling continuous updates by AD researchers.
Conclusions: AlzPathway is the first comprehensive map of intra, inter and extra cellular AD signaling pathways which can enable mechanistic deciphering of AD pathogenesis. The AlzPathway map is accessible at http://alzpathway.org/.
Figures

References
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease Interanational. World Alzheimer’s Report 2010. http://www.alz.co.uk/research/files/WorldAlzheimerReport2010ExecutiveSum....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

