A doxycycline-dependent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replicates in vivo without inducing CD4+ T-cell depletion
- PMID: 22647372
- PMCID: PMC3542129
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.042796-0
A doxycycline-dependent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replicates in vivo without inducing CD4+ T-cell depletion
Abstract
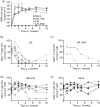
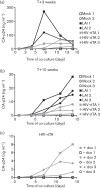
A novel genetic approach for the control of virus replication was used for the design of a conditionally replicating human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) variant, HIV-rtTA. HIV-rtTA gene expression and virus replication are strictly dependent on the presence of a non-toxic effector molecule, doxycycline (dox), and thus can be turned on and off at will in a graded and reversible manner. The in vivo replication capacity, pathogenicity and genetic stability of this HIV-rtTA variant were evaluated in a humanized mouse model of haematopoiesis that harbours lymphoid and myeloid components of the human immune system (HIS). Infection of dox-fed BALB Rag/γc HIS (BRG-HIS) mice with HIV-rtTA led to the establishment of a productive infection without CD4(+) T-cell depletion. The virus did not show any sign of escape from dox control for up to 10 weeks after the onset of infection. No reversion towards a functional Tat-transactivating responsive (TAR) RNA element axis was observed, confirming the genetic stability of the HIV-rtTA variant in vivo. These results demonstrate the proof of concept that HIV-rtTA replicates efficiently in vivo. HIV-rtTA is a promising tool for fundamental research to study virus-host interactions in vivo in a controlled fashion.
Figures



References
-
- An D. S., Poon B., Fang R. H. T., Weijer K., Blom B., Spits H., Chen I. S. Y., Uittenbogaart C. H. (2007). Use of a novel chimeric mouse model with a functionally active human immune system to study human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Clin Vaccine Immunol 14, 391–396 10.1128/CVI.00403-06 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baenziger S., Tussiwand R., Schlaepfer E., Mazzucchelli L., Heikenwalder M., Kurrer M. O., Behnke S., Frey J., Oxenius A. & other authors (2006). Disseminated and sustained HIV infection in CD34+ cord blood cell-transplanted Rag2−/−γ c−/− mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103, 15951–15956 10.1073/pnas.0604493103 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becker P. D., Legrand N., van Geelen C. M., Noerder M., Huntington N. D., Lim A., Yasuda E., Diehl S. A., Scheeren F. A. & other authors (2010). Generation of human antigen-specific monoclonal IgM antibodies using vaccinated “human immune system” mice. PLoS ONE 5, e13137 10.1371/journal.pone.0013137 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

