Treatment with the arginase inhibitor Nw-hydroxy-nor-L-arginine restores endothelial function in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis
- PMID: 22647483
- PMCID: PMC3446511
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3860
Treatment with the arginase inhibitor Nw-hydroxy-nor-L-arginine restores endothelial function in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Endothelial dysfunction (ED) participates to atherogenesis associated to rheumatoid arthritis. We recently reported increased arginase activity/expression in vessels from adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) rats. In the present study, we investigated the effects of a curative treatment with the arginase inhibitor Nw-hydroxy-nor-L-arginine (nor-NOHA) on vascular dysfunction in AIA rats.
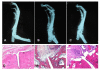
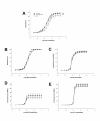
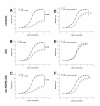
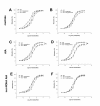
Methods: AIA rats were treated with nor-NOHA (40 mg/kg/d, ip) for 21 days after the onset of arthritis. A group of untreated AIA rats and a group of healthy rats served as controls. ED was assessed by the vasodilatory effect of acetylcholine (Ach) on aortic rings. The role of superoxide anions, prostanoids, endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) pathway was studied. Plasma levels of IL-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were determined by ELISA kits. Arthritis severity was estimated by a clinical, radiological and histological analysis.
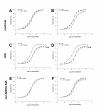
Results: Nor-NOHA treatment fully restored the aortic response to Ach to that of healthy controls. The results showed that this beneficial effect is mediated by an increase in NOS activity and EDHF and reduced superoxide anion production as well as a decrease in the activity of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, thromboxane and prostacyclins synthases. In addition, nor-NOHA decreased IL-6 and VEGF plasma levels in AIA rats. By contrast, the treatment did not modify arthritis severity in AIA rats.
Conclusions: The treatment with an arginase inhibitor has a potent effect on ED in AIA independently of the severity of the disease. Our results suggest that this new pharmacological approach has the potential as a novel add-on therapy in the treatment of RA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial dysfunction in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis: up-regulation of the vascular arginase pathway.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Aug;63(8):2309-17. doi: 10.1002/art.30391. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21484767
-
Diclofenac but not celecoxib improves endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis: A study in adjuvant-induced arthritis.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Nov;266:136-144. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.09.033. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 29024866
-
Glucocorticoids improve endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis: a study in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 May;188(2):208-218. doi: 10.1111/cei.12938. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28152574 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of animal models for identification of potential therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Nov;67(11):1505-15. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.076430. Epub 2007 Nov 29. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 18055474 Review.
-
Mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis: lessons from animal studies.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Jan 24;16(1):202. doi: 10.1186/ar4450. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24457026 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the eNOS Uncoupling and the Nitric Oxide Metabolic Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Apr 13;2020:1417981. doi: 10.1155/2020/1417981. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32351667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arginine Dysregulation and Myocardial Dysfunction in a Mouse Model and Children with Chronic Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 30;15(9):2162. doi: 10.3390/nu15092162. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432321 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian Arginase Inhibitory Activity of Methanolic Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Cyperus Species.Molecules. 2021 Mar 18;26(6):1694. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061694. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33803532 Free PMC article.
-
Amino Acid Metabolism in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Friend or Foe?Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 4;10(9):1280. doi: 10.3390/biom10091280. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32899743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Promising Arginase Inhibitors.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2017 Jun;42(3):355-370. doi: 10.1007/s13318-016-0381-y. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2017. PMID: 27734327 Review.
References
-
- Södergren A, Karp K, Boman K, Eriksson C, Lundström E, Smedby T, Söderlund L, Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, Wållberg-Jonsson S. Atherosclerosis in early rheumatoid arthritis: very early endothelial activation and rapid progression of intima media thickness. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R158. doi: 10.1186/ar3116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haruna Y, Morita Y, Komai N, Yada T, Sakuta T, Tomita N, Fox DA, Kashihara N. Endothelial dysfunction in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis:vascular superoxide production by NAD(P)H oxidase and uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1847–1855. doi: 10.1002/art.21891. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

