Specific elevation of DcR3 in sera of sepsis patients and its potential role as a clinically important biomarker of sepsis
- PMID: 22647538
- PMCID: PMC3396789
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2012.04.008
Specific elevation of DcR3 in sera of sepsis patients and its potential role as a clinically important biomarker of sepsis
Abstract
Because of its potentially important role in the pathogenesis of sepsis, the expression of soluble decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) was investigated in sera of sepsis patients. The serum levels of DcR3 and its tumor necrosis factor-like ligand TL1A and homologous decoy receptor OPG were quantified by ELISA. The values of DcR3 to diagnose sepsis were analyzed by receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves. The results showed that DcR3 was significantly elevated in sepsis compared to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), a condition similar to sepsis but resulting from noninfectious insults. DcR3 showed superior area under the ROC curve (AUC, 0.958) compared to poor AUCs of TL1A and OPG. At a cut-off of 3.24 ng/mL, DcR3 predicted sepsis from SIRS with 96% sensitivity and 82.6% specificity. DcR3 also predicted sepsis from cancer and inflammatory bowel disease with equally excellent values. Therefore, DcR3 serum level has the potential to serve as a reliable biomarker of sepsis.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
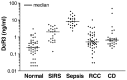
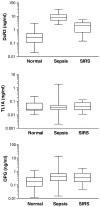
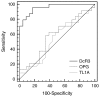
References
-
- American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1992;20:864–874. - PubMed
-
- Angus D.C., Linde-Zwirble W.T., Lidicker J., Clermont G., Carcillo J., Pinsky M.R. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Calich V.L., Pina A., Felonato M., Bernardino S., Costa T.A., Loures F.V. Toll-like receptors and fungal infections: the role of TLR2, TLR4 and MyD88 in paracoccidioidomycosis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008;53:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y.C., Hsu T.L., Lin H.H., Chio C.C., Chiu A.W., Chen N.J. Modulation of macrophage differentiation and activation by decoy receptor 3. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;75:486–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

