Sources of energy for gating by neurotransmitters in acetylcholine receptor channels
- PMID: 22647603
- PMCID: PMC3386111
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1203633109
Sources of energy for gating by neurotransmitters in acetylcholine receptor channels
Abstract
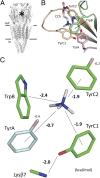
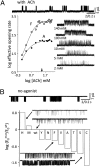
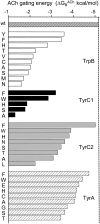
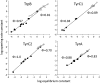
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) mediate signaling in the central and peripheral nervous systems. The AChR gating conformational change is powered by a low- to high-affinity change for neurotransmitters at two transmitter binding sites. We estimated (from single-channel currents) the components of energy for gating arising from binding site aromatic residues in the α-subunit. All mutations reduced the energy (TyrC1>>TrpB≈TyrC2>TyrA), with TyrC1 providing ~40% of the total. Considered one at a time, the fractional energy contributions from the aromatic rings were TrpB ~35%, TyrC1 ~28%, TyrC2 ~28%, and TyrA ~10%. Together, TrpB, TyrC1, and TyrC2 comprise an "aromatic triad" that provides much of the total energy from the transmitter for gating. Analysis of mutant pairs suggests that the energy contributions from some residues are nearly independent. Mutations of TyrC1 cause particularly large energy reductions because they remove two favorable and approximately equal interactions between the aromatic ring and the quaternary amine of the agonist and between the hydroxyl and αLysβ7.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of endplate nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by agonists.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;97(4):601-608. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.06.024. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26206191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional differences between neurotransmitter binding sites of muscle acetylcholine receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 9;111(49):17660-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1414378111. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25422413 Free PMC article.
-
The role of loop 5 in acetylcholine receptor channel gating.J Gen Physiol. 2003 Nov;122(5):521-39. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200308885. Epub 2003 Oct 13. J Gen Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14557402 Free PMC article.
-
Gating at the mouth of the acetylcholine receptor channel: energetic consequences of mutations in the alphaM2-cap.PLoS One. 2008 Jun 25;3(6):e2515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002515. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18575616 Free PMC article.
-
The gating isomerization of neuromuscular acetylcholine receptors.J Physiol. 2010 Feb 15;588(Pt 4):573-86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.182774. Epub 2009 Nov 23. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19933754 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The energy and work of a ligand-gated ion channel.J Mol Biol. 2013 May 13;425(9):1461-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.01.027. Epub 2013 Jan 25. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23357172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic activation of endplate acetylcholine receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 7;114(45):11914-11919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711228114. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29078356 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular recognition at cholinergic synapses: acetylcholine versus choline.J Physiol. 2017 Feb 15;595(4):1253-1261. doi: 10.1113/JP273291. Epub 2016 Dec 12. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27779761 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of endplate nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by agonists.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;97(4):601-608. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.06.024. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26206191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Agonist activation of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Sep;96(Pt B):150-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.10.004. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25446670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Noda M, et al. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983;302:528–532. - PubMed
-
- Unwin N. Refined structure of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at 4A resolution. J Mol Biol. 2005;346:967–989. - PubMed
-
- Brejc K, et al. Crystal structure of an ACh-binding protein reveals the ligand-binding domain of nicotinic receptors. Nature. 2001;411:269–276. - PubMed
-
- Cohen JB, Sharp SD, Liu WS. Structure of the agonist-binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. [3H]acetylcholine mustard identifies residues in the cation-binding subsite. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:23354–23364. - PubMed
-
- Dennis M, et al. Amino acids of the Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit labeled by a photoaffinity ligand for the acetylcholine binding site. Biochemistry. 1988;27:2346–2357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

