The class I PI3K/Akt pathway is critical for cancer cell survival in dogs and offers an opportunity for therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 22647622
- PMCID: PMC3515332
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-6148-8-73
The class I PI3K/Akt pathway is critical for cancer cell survival in dogs and offers an opportunity for therapeutic intervention
Abstract
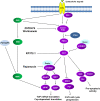
Background: Using novel small-molecular inhibitors, we explored the feasibility of the class I PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 signaling pathway as a therapeutic target in canine oncology either by using pathway inhibitors alone, in combination or combined with conventional chemotherapeutic drugs in vitro.
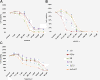
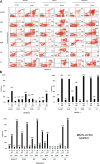
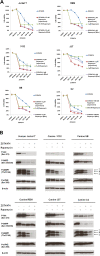
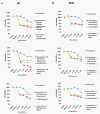
Results: We demonstrate that growth and survival of the cell lines tested are predominantly dependent on class I PI3K/Akt signaling rather than mTORC1 signaling. In addition, the newly developed inhibitors ZSTK474 and KP372-1 which selectively target pan-class I PI3K and Akt, respectively, and Rapamycin which has been well-established as highly specific mTOR inhibitor, decrease viability of canine cancer cell lines. All inhibitors demonstrated inhibition of phosphorylation of pathway members. Annexin V staining demonstrated that KP372-1 is a potent inducer of apoptosis whereas ZSTK474 and Rapamycin are weaker inducers of apoptosis. Simultaneous inhibition of class I PI3K and mTORC1 by ZSTK474 combined with Rapamycin additively or synergistically reduced cell viability whereas responses to the PI3K pathway inhibitors in combination with conventional drug Doxorubicin were cell line-dependent.
Conclusion: This study highlighted the importance of class I PI3K/Akt axis signaling in canine tumour cells and identifies it as a promising therapeutic target.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibition shows antileukemic activity in MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia.Leukemia. 2015 Apr;29(4):828-38. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.305. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Leukemia. 2015. PMID: 25322685
-
Anti-myeloma activity of Akt inhibition is linked to the activation status of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK pathway.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050005. Epub 2012 Nov 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23185517 Free PMC article.
-
A mechanism for synergy with combined mTOR and PI3 kinase inhibitors.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26343. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026343. Epub 2011 Oct 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22039466 Free PMC article.
-
Review: The PI3K-AKT-mTOR signal transduction pathway in canine cancer.Vet Pathol. 2024 May;61(3):339-356. doi: 10.1177/03009858231207021. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Vet Pathol. 2024. PMID: 37905509 Review.
-
Picking the point of inhibition: a comparative review of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 May;13(5):1021-31. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0639. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24748656 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of in vitro intrinsic radiosensitivity and characterization of five canine high-grade glioma cell lines.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Nov 30;10:1253074. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1253074. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38098992 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in triple negative feline mammary carcinomas.BMC Vet Res. 2013 Apr 15;9:80. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-9-80. BMC Vet Res. 2013. PMID: 23587222 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway in the tumorigenesis of canine thyroid carcinoma.J Vet Intern Med. 2014 Nov-Dec;28(6):1814-23. doi: 10.1111/jvim.12435. Epub 2014 Sep 17. J Vet Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 25231196 Free PMC article.
-
Roxarsone induces angiogenesis via PI3K/Akt signaling.Cell Biosci. 2016 Sep 28;6:54. doi: 10.1186/s13578-016-0119-1. eCollection 2016. Cell Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27708768 Free PMC article.
-
p-S6 as a Prognostic Biomarker in Canine Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 4;12(7):935. doi: 10.3390/biom12070935. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883491 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

