A dosimetric phantom study of dose accuracy and build-up effects using IMRT and RapidArc in stereotactic irradiation of lung tumours
- PMID: 22647680
- PMCID: PMC3403858
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-7-79
A dosimetric phantom study of dose accuracy and build-up effects using IMRT and RapidArc in stereotactic irradiation of lung tumours
Abstract
Background and purpose: Stereotactic lung radiotherapy (SLRT) has emerged as a curative treatment for medically inoperable patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and the use of intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and volumetric modulated arc treatments (VMAT) have been proposed as the best practical approaches for the delivery of SLRT. However, a large number of narrow field shapes are needed in the dose delivery of intensity-modulated techniques and the probability of underdosing the tumour periphery increases as the effective field size is decreased. The purpose of this study was to evaluate small lung tumour doses irradiated by intensity-modulated techniques to understand the risk for dose calculation errors in precision radiotherapy such as SLRT.
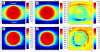
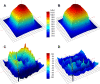
Materials and methods: The study was executed with two heterogeneous phantoms with targets of Ø1.5 and Ø4.0 cm. Dose distributions in the simulated tumours delivered by small sliding window apertures (SWAs), IMRT and RapidArc treatment plans were measured with radiochromic film. Calculation algorithms of pencil beam convolution (PBC) and anisotropic analytic algorithm (AAA) were used to calculate the corresponding dose distributions.
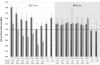
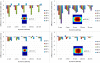
Results: Peripheral doses of the tumours were decreased as SWA decreased, which was not modelled by the calculation algorithms. The smallest SWA studied was 2 mm, which reduced the 90% isodose line width by 4.2 mm with the Ø4.0 cm tumour as compared to open field irradiation. PBC was not able to predict the dose accurately as the gamma evaluation failed to meet the criteria of ±3%/±1 mm on average in 61% of the defined volume with the smaller tumour. With AAA the corresponding value was 16%. The dosimetric inaccuracy of AAA was within ±3% with the optimized treatment plans of IMRT and RapidArc. The exception was the clinical RapidArc plan with dose overestimation of 4%.
Conclusions: Overall, the peripheral doses of the simulated lung tumours were decreased by decreasing the SWA. To achieve adequate surface dose coverage to small lung tumours with a difference less than 1 mm in the isodose line radius between the open and modulated field, a larger than 6 mm SWA should be used in the dose delivery of SLRT.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dosimetric accuracy and clinical quality of Acuros XB and AAA dose calculation algorithm for stereotactic and conventional lung volumetric modulated arc therapy plans.Radiat Oncol. 2013 Jun 24;8:149. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-8-149. Radiat Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23800024 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of dose calculation algorithms for static and rotational IMRT of lung cancer: A phantom study.Phys Med. 2015 Jun;31(4):382-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2015.02.013. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Phys Med. 2015. PMID: 25801284
-
Dosimetric impact of Acuros XB deterministic radiation transport algorithm for heterogeneous dose calculation in lung cancer.Med Phys. 2013 May;40(5):051710. doi: 10.1118/1.4802216. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23635258 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical application of a novel hybrid intensity-modulated radiotherapy technique for stage III lung cancer and dosimetric comparison with four other techniques.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Jun 1;83(2):e297-303. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.12.059. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22579380
-
Influence of the jaw tracking technique on the dose calculation accuracy of small field VMAT plans.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017 Jan;18(1):186-195. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12029. Epub 2017 Jan 3. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28291941 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A dosimetric phantom study of thoracic radiotherapy based on three-dimensional modeling of mediastinal lymph nodes.Oncol Lett. 2018 Apr;15(4):5634-5642. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8084. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29556300 Free PMC article.
-
A dosimetric evaluation of VMAT for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2012 Sep 1;14(1):4110. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v14i1.4110. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 23318374 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dosimetric evaluation of compensator intensity modulation-based stereotactic body radiotherapy for Stage I non-small-cell lung cancer.Br J Radiol. 2015 Aug;88(1052):20150122. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150122. Epub 2015 May 21. Br J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25996577 Free PMC article.
-
Chest wall toxicity after stereotactic radiation in early lung cancer: a systematic review.Curr Oncol. 2020 Aug;27(4):179-189. doi: 10.3747/co.27.5959. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Curr Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32905234 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric accuracy and clinical quality of Acuros XB and AAA dose calculation algorithm for stereotactic and conventional lung volumetric modulated arc therapy plans.Radiat Oncol. 2013 Jun 24;8:149. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-8-149. Radiat Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23800024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumann P, Nyman J, Hoyer M, Wennberg B, Gagliardi G, Lax I, Drugge N, Ekberg L, Friesland S, Johansson KA, Lund JA, Morhed E, Nilsson K, Levin N, Paludan M, Sederholm C, Traberg A, Wittgren L, Lewensohn R. Outcome in a prospective phase II trial of medically inoperable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3290–3296. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.5681. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Ruysscher D, Faivre-Finn C, Nestle U, Hurkmans CW, Le Péchoux C, Price A, Senan S. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer recommendations for planning and delivery of high-dose, high-precision radiotherapy for lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:5301–5310. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.3271. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fakiris AJ, McGarry RC, Yiannoutsos CT, Papiez L, Williams M, Henderson MA, Timmerman R. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early stage non-small cell lung carcinoma: Four-year results of a prospective phase II study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75:677–682. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.11.042. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

