The NOX toolbox: validating the role of NADPH oxidases in physiology and disease
- PMID: 22648375
- PMCID: PMC3383958
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-1010-9
The NOX toolbox: validating the role of NADPH oxidases in physiology and disease
Abstract
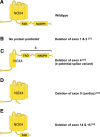
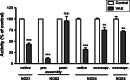
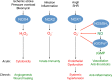
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are cellular signals but also disease triggers; their relative excess (oxidative stress) or shortage (reductive stress) compared to reducing equivalents are potentially deleterious. This may explain why antioxidants fail to combat diseases that correlate with oxidative stress. Instead, targeting of disease-relevant enzymatic ROS sources that leaves physiological ROS signaling unaffected may be more beneficial. NADPH oxidases are the only known enzyme family with the sole function to produce ROS. Of the catalytic NADPH oxidase subunits (NOX), NOX4 is the most widely distributed isoform. We provide here a critical review of the currently available experimental tools to assess the role of NOX and especially NOX4, i.e. knock-out mice, siRNAs, antibodies, and pharmacological inhibitors. We then focus on the characterization of the small molecule NADPH oxidase inhibitor, VAS2870, in vitro and in vivo, its specificity, selectivity, and possible mechanism of action. Finally, we discuss the validation of NOX4 as a potential therapeutic target for indications including stroke, heart failure, and fibrosis.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

