Residual disease detected by multidimensional flow cytometry signifies high relapse risk in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: a report from Children's Oncology Group
- PMID: 22649108
- PMCID: PMC3429302
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-408336
Residual disease detected by multidimensional flow cytometry signifies high relapse risk in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: a report from Children's Oncology Group
Abstract
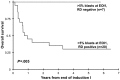
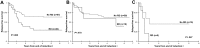
Early response to induction chemotherapy is a predictor of outcome in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). We determined the prevalence and significance of postinduction residual disease (RD) by multidimensional flow cytometry (MDF) in children treated on Children's Oncology Group AML protocol AAML03P1. Postinduction marrow specimens at the end of induction (EOI) 1 or 2 or at the end of therapy from 249 patients were prospectively evaluated by MDF for RD, and presence of RD was correlated with disease characteristics and clinical outcome. Of the 188 patients in morphologic complete remission at EOI1, 46 (24%) had MDF-detectable disease. Those with and without RD at the EOI1 had a 3-year relapse risk of 60% and 29%, respectively (P < .001); the corresponding relapse-free survival was 30% and 65% (P < .001). Presence of RD at the EOI2 and end of therapy was similarly predictive of poor outcome. RD was detected in 28% of standard-risk patients in complete remission and was highly associated with poor relapse-free survival (P = .008). In a multivariate analysis, including cytogenetic and molecular risk factors, RD was an independent predictor of relapse (P < .001). MDF identifies patients at risk of relapse and poor outcome and can be incorporated into clinical trials for risk-based therapy allocation. This study was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00070174.
Figures





Comment in
-
When it comes to MRD, AML ≠ ALL.Blood. 2012 Aug 23;120(8):1536-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-435081. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22918419
References
-
- Terstappen LW, Loken MR. Myeloid cell differentiation in normal bone marrow and acute myeloid leukemia assessed by multi-dimensional flow cytometry. Anal Cell Pathol. 1990;2(4):229–240. - PubMed
-
- Terstappen L, Loken M. Multi-dimensional flow cytometric characterization of myeloid maturation in normal bone marrow and acute myeloid leukemia. In: Burger G, Oberholzer M, Vooijs G, editors. Advances in Analytical Cellular Pathology. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Excerpta Medica; 1990. pp. 209–210.
-
- Wormann B SM, Konemann S, et al. Detection of residual leukemic cells in AML patients in complete remission [abstract]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 1991;78(11) Abstract 381.
-
- San Miguel JF, Martinez A, Macedo A, et al. Immunophenotyping investigation of minimal residual disease is a useful approach for predicting relapse in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Blood. 1997;90(6):2465–2470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

