VHL regulates the effects of miR-23b on glioma survival and invasion via suppression of HIF-1α/VEGF and β-catenin/Tcf-4 signaling
- PMID: 22649212
- PMCID: PMC3408255
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nos122
VHL regulates the effects of miR-23b on glioma survival and invasion via suppression of HIF-1α/VEGF and β-catenin/Tcf-4 signaling
Abstract
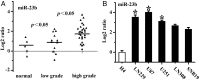
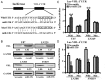
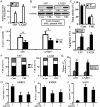
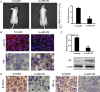
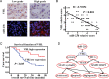
Aberrant microRNA expression has been implicated in the development of human cancers. Here, we investigated the oncogenic significance and function of miR-23b in glioma. We identified that the expression of miR-23b was elevated in both glioma samples and glioma cells, indicated by real-time polymerase chain reaction analyses. Down-regulation of miR-23b triggered growth inhibition, induced apoptosis, and suppressed invasion of glioma in vitro. Luciferase assay and Western blot analysis revealed that VHL is a direct target of miR-23b. Restoring expression of VHL inhibited glioma proliferation and invasion. Mechanistic investigation revealed that miR-23b deletion decreased HIF-1α/VEGF expression and suppressed β-catenin/Tcf-4 transcription activity by targeting VHL. Furthermore, expression of VHL was inversely correlated with miR-23b in glioma samples and was predictive of patient survival in a retrospective analysis. Therefore, we demonstrated that downregulation of miR-23b suppressed tumor survival through targeting VHL, leading to the inhibition of β-catenin/Tcf-4 and HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215–233. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120(1):15–20. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(11):857–866. doi:10.1038/nrc1997. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay S, Mitra R, Maulik U, Zhang MQ. Development of the human cancer microRNA network. Silence. 2010;1(1):6. doi:10.1186/1758-907X-1-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ. Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(3):166–193. doi:10.3322/caac.20069. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

