Fgf-dependent glial cell bridges facilitate spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish
- PMID: 22649227
- PMCID: PMC6703582
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0758-12.2012
Fgf-dependent glial cell bridges facilitate spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish
Abstract
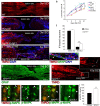
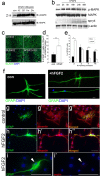
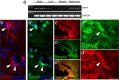
Adult zebrafish show a remarkable capacity to regenerate their spinal column after injury, an ability that stands in stark contrast to the limited repair that occurs within the mammalian CNS post-injury. The reasons for this interspecies difference in regenerative capacity remain unclear. Here we demonstrate a novel role for Fgf signaling during glial cell morphogenesis in promoting axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury. Zebrafish glia are induced by Fgf signaling, to form an elongated bipolar morphology that forms a bridge between the two sides of the resected spinal cord, over which regenerating axons actively migrate. Loss of Fgf function inhibits formation of this "glial bridge" and prevents axon regeneration. Despite the poor potential for mammalian axonal regeneration, primate astrocytes activated by Fgf signaling adopt a similar morphology to that induced in zebrafish glia. This suggests that differential Fgf regulation, rather than intrinsic cell differences, underlie the distinct responses of mammalian and zebrafish glia to injury.
Figures






References
-
- Barnabé-Heider F, Göritz C, Sabelströom H, Takebayashi H, Pfrieger FW, Meletis K, Frisén J. Origin of new glial cells in intact and injured adult spinal cord. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7:470–482. - PubMed
-
- Bastmeyer M, Bähr M, Stuermer CA. Fish optic nerve oligodendrocytes support axonal regeneration of fish and mammalian retinal ganglion cells. Glia. 1993;8:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Becker T, Wullimann MF, Becker CG, Bernhardt RR, Schachner M. Axonal regrowth after spinal cord transection in adult zebrafish. J Comp Neurol. 1997;377:577–595. - PubMed
-
- Bernardos RL, Raymond PA. GFAP transgenic zebrafish. Gene Expr Patterns. 2006;6:1007–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
