Increased frequency of circulating follicular helper T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 22649468
- PMCID: PMC3357937
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/827480
Increased frequency of circulating follicular helper T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
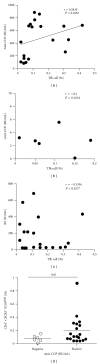
Follicular helper T (Tfh) cells are recognized as a distinct CD4(+) helper T-cell subset, which provides for B-cell activation and production of specific antibody responses, and play a critical role in the development of autoimmune disease. So far, only one study investigated the circulating Tfh cells increased in a subset of SLE patients. Since relatively little is known about the Tfh cells in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, in this study, Tfh-cell frequency, related cytokine IL-21, and transcription factor Bcl-6 were investigated in 53 patients with RA and 31 health controls. Firstly, we found that the frequency of CD4(+)CXCR5(+)ICOS(high) Tfh cells was increased significantly in the peripheral blood of RA patients, compared with that in healthy controls. It is known that Tfh cells are critical for directing the development of an antibody response by germinal centers B cells; secondly, we observed that the Tfh-cell frequency is accompanied by the level of anti-CCP antibody in RA patients. Furthermore, expression of Bcl-6 mRNA and plasma IL-21 concentrations in RA patients was increased. Taken together, these findings have shown that the increased frequency of circulating Tfh cells is correlated with elevated levels of anti-CCP antibody, indicating the possible involvement of Tfh cells in the disease progression of RA.
Figures


References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423(6937):356–361. - PubMed
-
- Fazilleau N, McHeyzer-Williams LJ, McHeyzer-Williams MG. Local development of effector and memory T helper cells. Current Opinion in Immunology. 2007;19(3):259–267. - PubMed
-
- Jacob J, Kelsoe G, Rajewsky K, Weiss U. Intraclonal generation of antibody mutants in germinal centres. Nature. 1991;354(6352):389–392. - PubMed
-
- Calame KL. Plasma cells: finding new light at the end of B cell development. Nature Immunology. 2001;2(12):1103–1108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

