Suppression of AP1 transcription factor function in keratinocyte suppresses differentiation
- PMID: 22649503
- PMCID: PMC3359321
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036941
Suppression of AP1 transcription factor function in keratinocyte suppresses differentiation
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Suppression of AP1 Transcription Factor Function in Keratinocyte Suppresses Differentiation.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 11;16(2):e0247222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247222. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33571274 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Our previous study shows that inhibiting activator protein one (AP1) transcription factor function in murine epidermis, using dominant-negative c-jun (TAM67), increases cell proliferation and delays differentiation. To understand the mechanism of action, we compare TAM67 impact in mouse epidermis and in cultured normal human keratinocytes. We show that TAM67 localizes in the nucleus where it forms TAM67 homodimers that competitively interact with AP1 transcription factor DNA binding sites to reduce endogenous jun and fos factor binding. Involucrin is a marker of keratinocyte differentiation that is expressed in the suprabasal epidermis and this expression requires AP1 factor interaction at the AP1-5 site in the promoter. TAM67 interacts competitively at this site to reduce involucrin expression. TAM67 also reduces endogenous c-jun, junB and junD mRNA and protein level. Studies with c-jun promoter suggest that this is due to reduced transcription of the c-jun gene. We propose that TAM67 suppresses keratinocyte differentiation by interfering with endogenous AP1 factor binding to regulator elements in differentiation-associated target genes, and by reducing endogenous c-jun factor expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
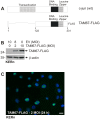

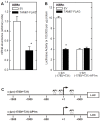
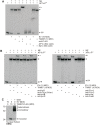
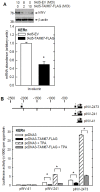
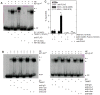
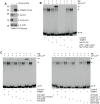
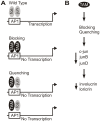
Comment in
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2024 Aug 15;89(158):66420-66422. Fed Regist. 2024. PMID: 39161428 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Angel P, Szabowski A, Schorpp-Kistner M. Function and regulation of AP-1 subunits in skin physiology and pathology. Oncogene. 2001;20:2413–2423. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Liu Z, Zandi E. AP-1 function and regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:240–246. - PubMed
-
- Shaulian E, Karin M. AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:E131–E136. - PubMed
-
- Shaulian E, Karin M. AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene. 2001;20:2390–2400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

