Impact of environmental parameters on marathon running performance
- PMID: 22649525
- PMCID: PMC3359364
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037407
Impact of environmental parameters on marathon running performance
Abstract
Purpose: The objectives of this study were to describe the distribution of all runners' performances in the largest marathons worldwide and to determine which environmental parameters have the maximal impact.
Methods: We analysed the results of six European (Paris, London, Berlin) and American (Boston, Chicago, New York) marathon races from 2001 to 2010 through 1,791,972 participants' performances (all finishers per year and race). Four environmental factors were gathered for each of the 60 races: temperature (°C), humidity (%), dew point (°C), and the atmospheric pressure at sea level (hPA); as well as the concentrations of four atmospheric pollutants: NO(2)-SO(2)-O(3) and PM(10) (μg x m(-3)).
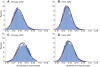
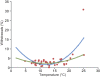
Results: All performances per year and race are normally distributed with distribution parameters (mean and standard deviation) that differ according to environmental factors. Air temperature and performance are significantly correlated through a quadratic model. The optimal temperatures for maximal mean speed of all runners vary depending on the performance level. When temperature increases above these optima, running speed decreases and withdrawal rates increase. Ozone also impacts performance but its effect might be linked to temperature. The other environmental parameters do not have any significant impact.
Conclusions: The large amount of data analyzed and the model developed in this study highlight the major influence of air temperature above all other climatic parameter on human running capacity and adaptation to race conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

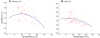
References
-
- Macarthur DG, North KN. Genes and human elite athletic performance. Hum Genet. 2005;116(5):331–339. - PubMed
-
- Cheuvront SN, Haymes EM. Thermoregulation and marathon running, biological and environmental influences. Sports Med. 2001;31(10):743–762. - PubMed
-
- Kenefick RW, Cheuvront SN, Sawka MN. Thermoregulatory function during the marathon. Sports Med. 2007;37(4–5):312–315. - PubMed
-
- Weather Underground website. Internet weather service. Weather data from each marathon race. 30 Available: http://www.wunderground.com/history/. Accessed 2011 Mar.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

