A Bioinformatics Resource for TWEAK-Fn14 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 22649723
- PMCID: PMC3357548
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/376470
A Bioinformatics Resource for TWEAK-Fn14 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
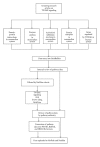
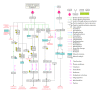
TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) is a new member of the TNF superfamily. It signals through TNFRSF12A, commonly known as Fn14. The TWEAK-Fn14 interaction regulates cellular activities including proliferation, migration, differentiation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, tissue remodeling and inflammation. Although TWEAK has been reported to be associated with autoimmune diseases, cancers, stroke, and kidney-related disorders, the downstream molecular events of TWEAK-Fn14 signaling are yet not available in any signaling pathway repository. In this paper, we manually compiled from the literature, in particular those reported in human systems, the downstream reactions stimulated by TWEAK-Fn14 interactions. Our manual amassment of the TWEAK-Fn14 pathway has resulted in cataloging of 46 proteins involved in various biochemical reactions and TWEAK-Fn14 induced expression of 28 genes. We have enabled the availability of data in various standard exchange formats from NetPath, a repository for signaling pathways. We believe that this composite molecular interaction pathway will enable identification of new signaling components in TWEAK signaling pathway. This in turn may lead to the identification of potential therapeutic targets in TWEAK-associated disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H, et al. TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997;272(51):32401–32410. - PubMed
-
- Novoyatleva T, Diehl F, Van Amerongen MJ, et al. TWEAK is a positive regulator of cardiomyocyte proliferation. Cardiovascular Research. 2010;85(4):681–690. - PubMed
-
- Ortiz A, Sanchez-Nino MD, Izquierdo MC, et al. TWEAK and the kidney: the dual role of a multifunctional cytokine. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 2011;691:323–335. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

