Imatinib enhances docetaxel-induced apoptosis through inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activation in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells
- PMID: 22650230
- PMCID: PMC3387763
- DOI: 10.1089/thy.2011.0380
Imatinib enhances docetaxel-induced apoptosis through inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activation in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: We previously reported the partial effectiveness of imatinib (also known as STI571, Glivec, or Gleevec) on anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) cells. Imatinib is a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor that has been used for various types of cancer treatments. Recently, several reports have demonstrated that imatinib enhanced the sensitivity of cancer cells to other anticancer drugs. In this study, therefore, we investigated whether imatinib enhances the antitumor activity of docetaxel in ATC cells.
Methods: Two ATC cell lines, FRO and KTC-2, were treated with imatinib and/or docetaxel. Cell survival assay and flow cytometry for annexin V were used to assess the induction of apoptosis. Changes of pro- and antiapoptotic factors were determined by Western blot. Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity was measured by DNA-binding assay. Tumor growth was also investigated in vivo.
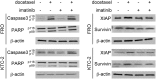
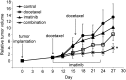
Results: The combined treatment significantly enhanced apoptosis compared with single treatment. ATC cells themselves expressed high levels of antiapoptotic factors, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP), and survivin. The treatment with docetaxel alone further increased their expressions; however, the combined treatment blocked the inductions. Although imatinib alone had no effect on NF-κB background levels, combined treatment significantly suppressed the docetaxel-induced NF-κB activation. Further, the combined administration of the drugs also showed significantly greater inhibitory effect on tumor growth in mice xenograft model.
Conclusions: Imatinib enhanced antitumor activity of docetaxel in ATC cells. Docetaxel seemed to induce both pro- and antiapoptotic signaling pathways in ATC cells, and imatinib blocked the antiapoptotic signal. Thus, docetaxel combined with imatinib emerges as an attractive strategy for the treatment of ATC.
Figures




References
-
- Brignardello E. Gallo M. Baldi I. Palestini N. Piovesan A. Grossi E. Ciccone G. Boccuzzi G. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: clinical outcome of 30 consecutive patients referred to a single institution in the past 5 years. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007;156:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Kim JC. Saha D. Cao Q. Choy H. Enhancement of radiation effects by combined docetaxel and flavopiridol treatment in lung cancer cells. Radiother Oncol. 2004;71:213–221. - PubMed
-
- Mason KA. Hunter NR. Milas M. Abbruzzese JL. Milas L. Docetaxel enhances tumor radioresponse in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:2431–2438. - PubMed
-
- Reiner T. de las Pozas A. Gomez LA. Perez-Stable C. Low dose combinations of 2-methoxyestradiol and docetaxel block prostate cancer cells in mitosis and increase apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2009;276:21–31. - PubMed
-
- Kawada K. Kitagawa K. Kamei S. Inada M. Mitsuma A. Sawaki M. Kikumori T. Fujimoto Y. Arima H. Imai T. Ando Y. The feasibility study of docetaxel in patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010;40:596–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

