Lipid nanoparticles for hepatic delivery of small interfering RNA
- PMID: 22652024
- PMCID: PMC3374058
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.05.002
Lipid nanoparticles for hepatic delivery of small interfering RNA
Abstract
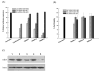
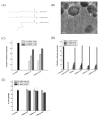
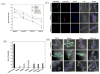
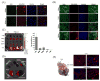
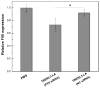
Clinical application of small interfering RNA (siRNA) requires safe and efficient delivery in vivo. Here, we report the design and synthesis of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for siRNA delivery based on cationic lipids with multiple tertiary amines and hydrophobic linoleyl chains. LNPs incorporating the lipid containing tris(2-aminoethyl)amine (TREN) and 3 linoleyl chains, termed TRENL3, were found to have exceptionally high siRNA transfection efficacy that was markedly superior to lipofectamine, a commercial transfection agent. In addition, inclusion of polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as linoleic acid and linolenic acid in the formulation further enhanced the siRNA delivery efficiency. TRENL3 LNPs were further shown to transport siRNA into the cytosol primarily via macropinocytosis rather than clathrin-mediated endocytosis. The new LNPs have demonstrated preferential uptake by the liver and hepatocellular carcinoma in mice, thereby leading to high siRNA gene-silencing activity. These data suggest potential therapeutic applications of TRENL3 mediated delivery of siRNA for liver diseases.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

