Astrocyte-derived VEGF-A drives blood-brain barrier disruption in CNS inflammatory disease
- PMID: 22653056
- PMCID: PMC3386814
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI60842
Astrocyte-derived VEGF-A drives blood-brain barrier disruption in CNS inflammatory disease
Abstract
In inflammatory CNS conditions such as multiple sclerosis (MS), current options to treat clinical relapse are limited, and more selective agents are needed. Disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is an early feature of lesion formation that correlates with clinical exacerbation, leading to edema, excitotoxicity, and entry of serum proteins and inflammatory cells. Here, we identify astrocytic expression of VEGF-A as a key driver of BBB permeability in mice. Inactivation of astrocytic Vegfa expression reduced BBB breakdown, decreased lymphocyte infiltration and neuropathology in inflammatory and demyelinating lesions, and reduced paralysis in a mouse model of MS. Knockdown studies in CNS endothelium indicated activation of the downstream effector eNOS as the principal mechanism underlying the effects of VEGF-A on the BBB. Systemic administration of the selective eNOS inhibitor cavtratin in mice abrogated VEGF-A-induced BBB disruption and pathology and protected against neurologic deficit in the MS model system. Collectively, these data identify blockade of VEGF-A signaling as a protective strategy to treat inflammatory CNS disease.
Figures



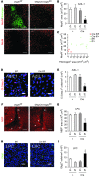
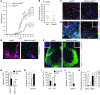
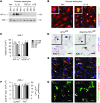
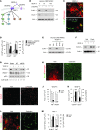

References
-
- Wolburg H, et al. Localization of claudin-3 in tight junctions of the blood-brain barrier is selectively lost during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and human glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neuropathol. 2003;105(6):586–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 NS051147/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS056074/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201000054C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32NS051147-03/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RG4127/RG/CSR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS056074/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057624/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS046620/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RG3874/RG/CSR NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS057624/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R24 CA095823/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS046620/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R24CA095823/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS062703/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS062703/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

