Comparative effects of low-carbohydrate high-protein versus low-fat diets on the kidney
- PMID: 22653255
- PMCID: PMC3386674
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.11741111
Comparative effects of low-carbohydrate high-protein versus low-fat diets on the kidney
Abstract
Background and objectives: Concerns exist about deleterious renal effects of low-carbohydrate high-protein weight loss diets. This issue was addressed in a secondary analysis of a parallel randomized, controlled long-term trial.
Design, setting, participants, and measurements: Between 2003 and 2007, 307 obese adults without serious medical illnesses at three United States academic centers were randomly assigned to a low-carbohydrate high-protein or a low-fat weight-loss diet for 24 months. Main outcomes included renal filtration (GFR) indices (serum creatinine, cystatin C, creatinine clearance); 24-hour urinary volume; albumin; calcium excretion; and serum solutes at 3, 12, and 24 months.
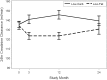
Results: Compared with the low-fat diet, low-carbohydrate high-protein consumption was associated with minor reductions in serum creatinine (relative difference, -4.2%) and cystatin C (-8.4%) at 3 months and relative increases in creatinine clearance at 3 (15.8 ml/min) and 12 (20.8 ml/min) months; serum urea at 3 (14.4%), 12 (9.0%), and 24 (8.2%) months; and 24-hour urinary volume at 12 (438 ml) and 24 (268 ml) months. Urinary calcium excretion increased at 3 (36.1%) and 12 (35.7%) months without changes in bone density or clinical presentations of new kidney stones.
Conclusions: In healthy obese individuals, a low-carbohydrate high-protein weight-loss diet over 2 years was not associated with noticeably harmful effects on GFR, albuminuria, or fluid and electrolyte balance compared with a low-fat diet. Further follow-up is needed to determine even longer-term effects on kidney function.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00143936.
Figures
References
-
- Sacks FM, Bray GA, Carey VJ, Smith SR, Ryan DH, Anton SD, McManus K, Champagne CM, Bishop LM, Laranjo N, Leboff MS, Rood JC, de Jonge L, Greenway FL, Loria CM, Obarzanek E, Williamson DA: Comparison of weight-loss diets with different compositions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. N Engl J Med 360: 859–873, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Foster GD, Wyatt HR, Hill JO, McGuckin BG, Brill C, Mohammed BS, Szapary PO, Rader DJ, Edman JS, Klein S: A randomized trial of a low-carbohydrate diet for obesity. N Engl J Med 348: 2082–2090, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Samaha FF, Iqbal N, Seshadri P, Chicano KL, Daily DA, McGrory J, Williams T, Williams M, Gracely EJ, Stern L: A low-carbohydrate as compared with a low-fat diet in severe obesity. N Engl J Med 348: 2074–2081, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Shai I, Schwarzfuchs D, Henkin Y, Shahar DR, Witkow S, Greenberg I, Golan R, Fraser D, Bolotin A, Vardi H, Tangi-Rozental O, Zuk-Ramot R, Sarusi B, Brickner D, Schwartz Z, Sheiner E, Marko R, Katorza E, Thiery J, Fiedler GM, Blüher M, Stumvoll M, Stampfer MJ, Dietary Intervention Randomized Controlled Trial (DIRECT) Group : Weight loss with a low-carbohydrate, Mediterranean, or low-fat diet. N Engl J Med 359: 229–241, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Gardner CD, Kiazand A, Alhassan S, Kim S, Stafford RS, Balise RR, Kraemer HC, King AC: Comparison of the Atkins, Zone, Ornish, and LEARN diets for change in weight and related risk factors among overweight premenopausal women: The A TO Z Weight Loss Study: a randomized trial. JAMA 297: 969–977, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical