Upregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 correlated with synovitis severity in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 22656185
- PMCID: PMC3446516
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3866
Upregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 correlated with synovitis severity in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease leading to joint destruction and disability. Focal bone erosion is due to excess bone resorption of osteoclasts. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) is one of the critical mediators both in inflammatory signal pathway and differentiation and resorption activity of osteoclasts. Here we aimed to investigate TRAF6 expression in RA synovium and its correlation with histological synovitis severity and radiological joint destruction in RA.
Methods: Synovitis score was determined in needle biopsied synovium from 44 patients with active RA. Synovium from nine patients with osteoarthritis (OA) and seven with orthopedic arthropathies (Orth.A) were enrolled as "less inflamed" disease controls. Serial sections were stained immunohistochemically for TRAF6 as well as CD68 (macrophage), CD3 (T cell), CD20 (B cell), CD38 (plasmocyte), CD79a (B lineage cells from pre-B cell to plasmocyte stage), and CD34 (endothelial cell). Double immunofluorescence staining of TRAF6 and CD68 were tested. Densities of positive staining cells were determined and correlated with histological disease activity (synovitis score) and radiographic joint destruction (Sharp score).
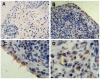
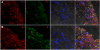
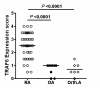
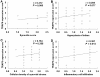
Results: TRAF6 expression was found in the intimal and subintimal area of RA synovium, with intense staining found in the endochylema and nucleus of intimal synoviocytes and subintimal inflammatory cells. Double immunofluorescence staining showed TRAF6 was expressed in most of the intimal cells and obviously expressed in CD68+ cells and some other CD68- cells in subintimal area. Synovial TRAF6 was significantly over-expressed in the RA group compared with the OA and Orth.A group (2.53 ± 0.94 vs. 0.72 ± 0.44 and 0.71 ± 0.49, P < 0.0001). Synovial TRAF6 expression in RA correlated significantly with synovitis score (r = 0.412, P = 0.006), as well as the inflammatory cell infiltration (r = 0.367, P = 0.014). Significant correlation was detected between synovial TRAF6 expression and intimal CD68+ cells, as well as the cell density of subintimal CD68+ cells, CD3+ cells, CD20+ cells, CD38+ cells, and CD79a+ cells (all P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Elevated synovial TRAF6 expression correlated with synovitis severity and CD68+ cell density in RA. It is, therefore, hypothesized that synovial TRAF6 is involved in the pathogenesis of synovial inflammation and osteoclast differentiation in RA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synovial infiltration with CD79a-positive B cells, but not other B cell lineage markers, correlates with joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2011 Nov;38(11):2301-8. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.110615. Epub 2011 Oct 15. J Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 22002013
-
Subintimal Ki-67 as a synovial tissue biomarker for inflammatory arthropathies.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Feb;67(2):162-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.071670. Epub 2007 Jul 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 17613556
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6 inhibition mitigates the pro-inflammatory roles and proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Cytokine. 2017 May;93:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 12. Cytokine. 2017. PMID: 28506571
-
Morphological and molecular pathology of the B cell response in synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis.Virchows Arch. 2002 Nov;441(5):415-27. doi: 10.1007/s00428-002-0702-1. Epub 2002 Nov 5. Virchows Arch. 2002. PMID: 12447670 Review.
-
Involvement of receptor activator of NFkappaB ligand and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.Bone. 2002 Feb;30(2):340-6. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00682-2. Bone. 2002. PMID: 11856640 Review.
Cited by
-
miRNAs and NFKB1 and TRAF6 target genes: The initial functional study in CD14+ monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Genet Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 26;47(2):e20230235. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2023-0235. eCollection 2024. Genet Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39058384 Free PMC article.
-
The Effective Treatment of Purpurin on Inflammation and Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis.Molecules. 2023 Jan 2;28(1):366. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010366. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36615560 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretation of immunohistochemistry data of tumor should consider microenvironmental factors.Tumour Biol. 2015 Jun;36(6):4467-77. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3088-9. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25753476
-
Targeting TRAF6 E3 ligase activity with a small-molecule inhibitor combats autoimmunity.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 24;293(34):13191-13203. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002649. Epub 2018 Jun 27. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29950522 Free PMC article.
-
A TRAF6 genetic variant is associated with low bone mineral density in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2019 Apr;38(4):1067-1074. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4362-1. Epub 2018 Dec 1. Clin Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30506403
References
-
- Kirwan JR. Links between radiological change, disability, and pathology in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:881–886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

