Caspase-11 promotes the fusion of phagosomes harboring pathogenic bacteria with lysosomes by modulating actin polymerization
- PMID: 22658523
- PMCID: PMC3408798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.05.001
Caspase-11 promotes the fusion of phagosomes harboring pathogenic bacteria with lysosomes by modulating actin polymerization
Abstract
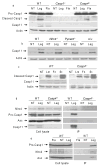
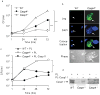
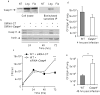
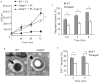
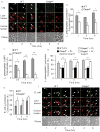
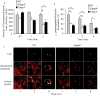
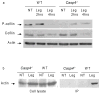
Inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes that include members of the NLR (nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat containing) family and caspase-1. Once bacterial molecules are sensed within the macrophage, the inflammasome is assembled, mediating the activation of caspase-1. Caspase-11 mediates caspase-1 activation in response to lipopolysaccharide and bacterial toxins, and yet its role during bacterial infection is unknown. Here, we demonstrated that caspase-11 was dispensable for caspase-1 activation in response to Legionella, Salmonella, Francisella, and Listeria. We also determined that active mouse caspase-11 was required for restriction of L. pneumophila infection. Similarly, human caspase-4 and caspase-5, homologs of mouse caspase-11, cooperated to restrict L. pneumophila infection in human macrophages. Caspase-11 promoted the fusion of the L. pneumophila vacuole with lysosomes by modulating actin polymerization through cofilin. However, caspase-11 was dispensable for the fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes containing nonpathogenic bacteria, uncovering a fundamental difference in the trafficking of phagosomes according to their cargo.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abdulrahman BA, Abu Khweek A, Akhter A, Caution K, Kotrange S, Abdelaziz DHA, Newland C, Rosales-Reyes R, Kopp B, McCoy K, et al. Autophagy stimulation by Rapamycin suppresses lung inflammation and infection by Burkholderia cenocepacia in a model of cystic fibrosis Autophagy. 2011. p. 7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amer A, Franchi L, Kanneganti TD, Body-Malapel M, Ozoren N, Brady G, Meshinchi S, Jagirdar R, Gewirtz A, Akira S, et al. Regulation of Legionella phagosome maturation and infection through flagellin and host Ipaf. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:35217–35223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

