Genetic architecture of microRNA expression: implications for the transcriptome and complex traits
- PMID: 22658545
- PMCID: PMC3370272
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.04.023
Genetic architecture of microRNA expression: implications for the transcriptome and complex traits
Abstract
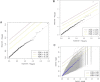
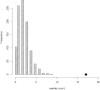
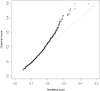
We sought to comprehensively and systematically characterize the relationship between genetic variation, miRNA expression, and mRNA expression. Genome-wide expression profiling of samples of European and African ancestry identified in each population hundreds of miRNAs whose increased expression is correlated with correspondingly reduced expression of target mRNAs. We scanned 3' UTR SNPs with a potential functional effect on miRNA binding for cis-acting expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) for the corresponding proximal target genes. To extend sequence-based, localized analyses of SNP effect on miRNA binding, we proceeded to dissect the genetic basis of miRNA expression variation; we mapped miRNA expression levels-as quantitative traits-to loci in the genome as miRNA eQTLs, demonstrating that miRNA expression is under significant genetic control. We found that SNPs associated with miRNA expression are significantly enriched with those SNPs already shown to be associated with mRNA. Moreover, we discovered that many of the miRNA-associated genetic variations identified in our study are associated with a broad spectrum of human complex traits from the National Human Genome Research Institute catalog of published genome-wide association studies. Experimentally, we replicated miRNA-induced mRNA expression inhibition and the cis-eQTL relationship to the target gene for several identified relationships among SNPs, miRNAs, and mRNAs in an independent set of samples; furthermore, we conducted miRNA overexpression and inhibition experiments to functionally validate the miRNA-mRNA relationships. This study extends our understanding of the genetic regulation of the transcriptome and suggests that genetic variation might underlie observed relationships between miRNAs and mRNAs more commonly than has previously been appreciated.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


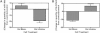

Similar articles
-
Genetic architecture of microRNA expression and its link to complex diseases in the Japanese population.Hum Mol Genet. 2022 Jun 4;31(11):1806-1820. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab361. Hum Mol Genet. 2022. PMID: 34919704 Free PMC article.
-
MirSNP, a database of polymorphisms altering miRNA target sites, identifies miRNA-related SNPs in GWAS SNPs and eQTLs.BMC Genomics. 2012 Nov 23;13:661. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-661. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23173617 Free PMC article.
-
Pinpointing miRNA and genes enrichment over trait-relevant tissue network in Genome-Wide Association Studies.BMC Med Genomics. 2020 Dec 28;13(Suppl 11):191. doi: 10.1186/s12920-020-00830-w. BMC Med Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33371893 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Information Improves Predictive Modeling of Disease Relevance of Non-Coding Genetic Variation.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 16;10(10):e0140758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140758. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26474488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determining causality and consequence of expression quantitative trait loci.Hum Genet. 2014 Jun;133(6):727-35. doi: 10.1007/s00439-014-1446-0. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24770875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA biogenesis and cellular proliferation.Transl Res. 2015 Aug;166(2):145-51. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2015.01.012. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 25724890 Free PMC article.
-
Omics Application in Animal Science-A Special Emphasis on Stress Response and Damaging Behaviour in Pigs.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 11;11(8):920. doi: 10.3390/genes11080920. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32796712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Needles in the genetic haystack of lipid disorders: single nucleotide polymorphisms in the microRNA regulome.J Lipid Res. 2013 May;54(5):1168-73. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R035766. Epub 2013 Mar 15. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23505316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative analyses of genetic variation, epigenetic regulation, and the transcriptome to elucidate the biology of platinum sensitivity.BMC Genomics. 2014 Apr 16;15:292. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-292. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24739237 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Gene Expression in Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014 Oct 23;5(8):a017210. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a017210. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014. PMID: 25342062 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

