CheA-receptor interaction sites in bacterial chemotaxis
- PMID: 22659323
- PMCID: PMC3418421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.05.023
CheA-receptor interaction sites in bacterial chemotaxis
Abstract
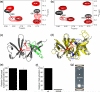
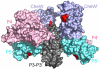
In bacterial chemotaxis, transmembrane chemoreceptors, the CheA histidine kinase, and the CheW coupling protein assemble into signaling complexes that allow bacteria to modulate their swimming behavior in response to environmental stimuli. Among the protein-protein interactions in the ternary complex, CheA-CheW and CheW-receptor interactions were studied previously, whereas CheA-receptor interaction has been less investigated. Here, we characterize the CheA-receptor interaction in Thermotoga maritima by NMR spectroscopy and validate the identified receptor binding site of CheA in Escherichia coli chemotaxis. We find that CheA interacts with a chemoreceptor in a manner similar to that of CheW, and the receptor binding site of CheA's regulatory domain is homologous to that of CheW. Collectively, the receptor binding sites in the CheA-CheW complex suggest that conformational changes in CheA are required for assembly of the CheA-CheW-receptor ternary complex and CheA activation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Wadhams GH, Armitage JP. Making sense of it all: bacterial chemotaxis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004;5:1024–1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

