Pulmonary microRNA profiling in a mouse model of ventilator-induced lung injury
- PMID: 22659882
- PMCID: PMC3423863
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00370.2011
Pulmonary microRNA profiling in a mouse model of ventilator-induced lung injury
Abstract
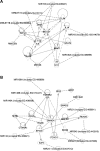
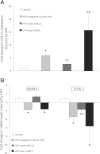
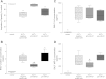
The aim of this study was to investigate the changes induced by high tidal volume ventilation (HVTV) in pulmonary expression of micro-RNAs (miRNAs) and identify potential target genes and corresponding miRNA-gene networks. Using a real-time RT-PCR-based array in RNA samples from lungs of mice subjected to HVTV for 1 or 4 h and control mice, we identified 65 miRNAs whose expression changed more than twofold upon HVTV. An inflammatory and a TGF-β-signaling miRNA-gene network were identified by in silico pathway analysis being at highest statistical significance (P = 10(-43) and P = 10(-28), respectively). In the inflammatory network, IL-6 and SOCS-1, regulated by miRNAs let-7 and miR-155, respectively, appeared as central nodes. In TGF-β-signaling network, SMAD-4, regulated by miR-146, appeared as a central node. The contribution of miRNAs to the development of lung injury was evaluated in mice subjected to HVTV treated with a precursor or antagonist of miR-21, a miRNA highly upregulated by HVTV. Lung compliance was preserved only in mice treated with anti-miR-21 but not in mice treated with pre-miR-21 or negative-control miRNA. Both alveolar-arterial oxygen difference and protein levels in bronchoalveolar lavage were lower in mice treated with anti-miR-21 than in mice treated with pre-miR-21 or negative-control miRNA (D(A-a): 66 ± 27 vs. 131 ± 22, 144 ± 10 mmHg, respectively, P < 0.001; protein concentration: 1.1 ± 0.2 vs. 2.3 ± 1, 2.1 ± 0.4 mg/ml, respectively, P < 0.01). Our results show that HVTV induces changes in miRNA expression in mouse lungs. Modulation of miRNA expression can affect the development of HVTV-induced lung injury.
Figures


References
-
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network Ventilation with lower tidal volumes compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury, and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 342: 1301–1308, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Barbieri SS, Ruggiero L, Tremoli E, Weksler BB. Suppressing PTEN activity by tobacco smoke plus interleukin-1beta modulates dissociation of VE-cadherin/beta-catenin complexes in endothelium. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28: 732–738, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

