Rational regulation of learning dynamics by pupil-linked arousal systems
- PMID: 22660479
- PMCID: PMC3386464
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3130
Rational regulation of learning dynamics by pupil-linked arousal systems
Abstract
The ability to make inferences about the current state of a dynamic process requires ongoing assessments of the stability and reliability of data generated by that process. We found that these assessments, as defined by a normative model, were reflected in nonluminance-mediated changes in pupil diameter of human subjects performing a predictive-inference task. Brief changes in pupil diameter reflected assessed instabilities in a process that generated noisy data. Baseline pupil diameter reflected the reliability with which recent data indicate the current state of the data-generating process and individual differences in expectations about the rate of instabilities. Together these pupil metrics predicted the influence of new data on subsequent inferences. Moreover, a task- and luminance-independent manipulation of pupil diameter predictably altered the influence of new data. Thus, pupil-linked arousal systems can help to regulate the influence of incoming data on existing beliefs in a dynamic environment.
Figures



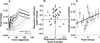
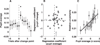


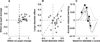
Comment in
-
Change is in the eye of the beholder.Nat Neurosci. 2012 Jun 26;15(7):933-5. doi: 10.1038/nn.3150. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22735513 No abstract available.
References
-
- Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Walton ME, Rushworth MF. Learning the value of information in an uncertain world. Nat. Neurosci. 2007;10:1214–1221. - PubMed
-
- Yu AJ, Dayan P. Uncertainty, neuromodulation, and attention. Neuron. 2005;46:681–692. - PubMed
-
- Aston–Jones G, Cohen JD. An integrative theory of locus coeruleus–norepinephrine function: adaptive gain and optimal performance. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2005;28:403–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

