Vascular leak is a central feature in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 22660809
- PMCID: PMC3640272
- DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.111380
Vascular leak is a central feature in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis
Abstract
Objective: The main histopathological focus of systemic sclerosis (SSc) has concentrated on fibrotic changes. We investigated the microvasculature alterations in the skin of patients with SSc at various stages of disease duration with whole-field digital microscopy.
Methods: Twenty consecutive patients with SSc, 1 with Raynaud's phenomenon (RP) without SSc, and 4 healthy controls underwent punch biopsy on the medial forearm. Eighteen patients were included in the primary analysis. Two with recent-onset diffuse cutaneous disease, 1 repeat SSc biopsy, and 1 patient with RP without SSc were also evaluated. All specimens were processed with histochemical stains and immunohistochemistry. We analyzed microvasculature abnormalities in an objective and systematic manner taking advantage of recent advances in whole-field digital microscopy. This analysis was coupled with ultrastructural evaluation performed with transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
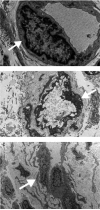
Results: Whole-field digital microscopy and TEM of SSc skin biopsies revealed that endothelial abnormalities are a universal feature regardless of clinical features and/or duration of disease. These features were not seen in any healthy control specimens or in the single RP patient samples. Whole-field digital microscopy identified increased interstitial edema (31.0% ± 9.6% vs 17.6% ± 3.3% in controls; p = 0.009) and fibrosis (75.6% ± 5.7% vs 66.1% ± 9.8% in controls; p = 0.02) in all patients with SSc. Lower CD34 staining was seen in SSc compared to healthy controls (0.32% ± 0.22% vs 1.31% ± 0.34%; p < 0.0001) and within the SSc population with interstitial lung disease (0.55% ± 0.22% vs 0.15% ± 0.16%; p = 0.01). Perivascular and interstitial infiltrate of mast cells was present in all SSc specimens.
Conclusion: Whole-field digital microscopy offers a means of rapidly carrying out objective, fully quantitative, and reproducible measurements of microscopic features of SSc microvascular change. The universal morphologically abnormal endothelial cells and interstitial edema in all patients with SSc biopsied suggests that SSc may be intrinsically a disease of the endothelium characterized by vascular leak.
Figures

References
-
- Chizzolini C, Brembilla NC, Montanari E, Truchetet ME. Fibrosis and immune dysregulation in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:276–81. - PubMed
-
- Jinnin M. Mechanisms of skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. J Dermatol. 2010;37:11–25. - PubMed
-
- Krieg T, Takehara K. Skin disease: A cardinal feature of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology. 2009;48(Suppl 3):iii14–8. - PubMed
-
- Pannu J, Trojanowska M. Recent advances in fibroblast signaling and biology in scleroderma. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004;16:739–45. - PubMed
-
- Jimenez SA, Hitraya E, Varga J. Pathogenesis of scleroderma. Collagen. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1996;22:647–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
