Critical evaluation of the efficacy and tolerability of azilsartan
- PMID: 22661897
- PMCID: PMC3363145
- DOI: 10.2147/VHRM.S22589
Critical evaluation of the efficacy and tolerability of azilsartan
Erratum in
- Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2012;8:443-5
Abstract
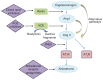
Appropriate control of blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive patients still represents the major therapeutic goal in the treatment of hypertension. Despite the growing attention and wide range of antihypertensive agents available in the clinical scenario, the target of BP below the advised thresholds of 140/90 mmHg is, unfortunately, often unreached. For this reason, the search for new antihypertensive agents is still ongoing. Azilsartan medoxomil, a new angiotensin receptor blocker that has been recently introduced in the clinical arena, represents the eighth angiotensin receptor blocker currently available for BP control. The aim of this paper is to describe the efficacy and safety profile of this new compound, reviewing available data obtained from both pre-clinical and clinical studies.
Keywords: angiotensin receptor blocker; azilsartan medoxomil; hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- Rosendorff C, Black HR, Cannon CP, et al. Treatment of hypertension in the prevention and management of ischemic heart disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Council for High Blood Pressure Research and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2007;115(21):2761–2788. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Reddy S, Ounpuu S, Anand S. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases: part I: general considerations, the epidemiologic transition, risk factors, and impact of urbanization. Circulation. 2001;104(22):2746–2753. - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217–223. - PubMed
-
- Guilbert JJ. The world health report 2002 – reducing risks, promoting healthy life. Educ Health (Abingdon) 2003;16(2):230. - PubMed
-
- Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A. International Society of Hypertension. Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet. 2008;371(9623):1513–1518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical