Radiation induces acute alterations in neuronal function
- PMID: 22662188
- PMCID: PMC3360766
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037677
Radiation induces acute alterations in neuronal function
Abstract
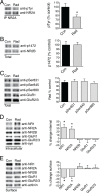
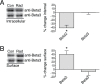
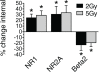
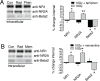
Every year, nearly 200,000 patients undergo radiation for brain tumors. For both patients and caregivers the most distressing adverse effect is impaired cognition. Efforts to protect against this debilitating effect have suffered from inadequate understanding of the cellular mechanisms of radiation damage. In the past it was accepted that radiation-induced normal tissue injury resulted from a progressive reduction in the survival of clonogenic cells. Moreover, because radiation-induced brain dysfunction is believed to evolve over months to years, most studies have focused on late changes in brain parenchyma. However, clinically, acute changes in cognition are also observed. Because neurons are fully differentiated post-mitotic cells, little information exists on the acute effects of radiation on synaptic function. The purpose of our study was to assess the potential acute effects of radiation on neuronal function utilizing ex vivo hippocampal brain slices. The cellular localization and functional status of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors was identified by immunoblotting. Electrophysiological recordings were obtained both for populations of neuronal cells and individual neurons. In the dentate gyrus region of isolated ex vivo slices, radiation led to early decreases in tyrosine phosphorylation and removal of excitatory N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) from the cell surface while simultaneously increasing the surface expression of inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors (GABA(A)Rs). These alterations in cellular localization corresponded with altered synaptic responses and inhibition of long-term potentiation. The non-competitive NMDAR antagonist memantine blocked these radiation-induced alterations in cellular distribution. These findings demonstrate acute effects of radiation on neuronal cells within isolated brain slices and open new avenues for study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Mulhern RK, Merchant TE, Gajjar A, Reddick WE, Kun LE. Late neurocognitive sequelae in survivors of brain tumours in childhood. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:399–408. - PubMed
-
- Crossen JR, Garwood D, Glatstein E, Neuwelt EA. Neurobehavioral sequelae of cranial irradiation in adults: a review of radiation-induced encephalopathy. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12:627–642. - PubMed
-
- Sun A, Bae K, Gore EM, Movsas B, Wong SJ, et al. J Clin Oncol 29: 279–286. Epub 2010 Dec 2016; 2011. Phase III trial of prophylactic cranial irradiation compared with observation in patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: neurocognitive and quality-of-life analysis. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:1037–1044. - PubMed
-
- Meyers CA, Brown PD. Role and relevance of neurocognitive assessment in clinical trials of patients with CNS tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1305–1309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

