Diurnal rhythms in neurexins transcripts and inhibitory/excitatory synapse scaffold proteins in the biological clock
- PMID: 22662246
- PMCID: PMC3360661
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037894
Diurnal rhythms in neurexins transcripts and inhibitory/excitatory synapse scaffold proteins in the biological clock
Abstract
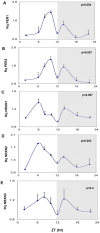
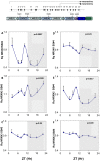
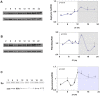
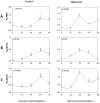
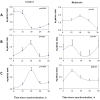
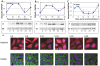
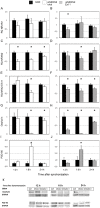
The neurexin genes (NRXN1/2/3) encode two families (α and β) of highly polymorphic presynaptic proteins that are involved in excitatory/inhibitory synaptic balance. Recent studies indicate that neuronal activation and memory formation affect NRXN1/2/3α expression and alternative splicing at splice sites 3 and 4 (SS#3/SS#4). Neurons in the biological clock residing in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus (SCN) act as self-sustained oscillators, generating rhythms in gene expression and electrical activity, to entrain circadian bodily rhythms to the 24 hours day/night cycles. Cell autonomous oscillations in NRXN1/2/3α expression and SS#3/SS#4 exons splicing and their links to rhythms in excitatory/inhibitory synaptic balance in the circadian clock were explored. NRXN1/2/3α expression and SS#3/SS#4 splicing, levels of neurexin-2α and the synaptic scaffolding proteins PSD-95 and gephyrin (representing excitatory and inhibitory synapses, respectively) were studied in mRNA and protein extracts obtained from SCN of C3H/J mice at different times of the 24 hours day/night cycle. Further studies explored the circadian oscillations in these components and causality relationships in immortalized rat SCN2.2 cells. Diurnal rhythms in mNRXN1α and mNRXN2α transcription, SS#3/SS#4 exon-inclusion and PSD-95 gephyrin and neurexin-2α levels were found in the SCN in vivo. No such rhythms were found with mNRXN3α. SCN2.2 cells also exhibited autonomous circadian rhythms in rNRXN1/2 expression SS#3/SS#4 exon inclusion and PSD-95, gephyrin and neurexin-2α levels. rNRXN3α and rNRXN1/2β were not expressed. Causal relationships were demonstrated, by use of specific siRNAs, between rNRXN2α SS#3 exon included transcripts and gephyrin levels in the SCN2.2 cells. These results show for the first time dynamic, cell autonomous, diurnal rhythms in expression and splicing of NRXN1/2 and subsequent effects on the expression of neurexin-2α and postsynaptic scaffolding proteins in SCN across the 24-h cycle. NRXNs gene transcripts may have a role in coupling the circadian clock to diurnal rhythms in excitatory/inhibitory synaptic balance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
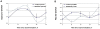
References
-
- Ushkaryov YA, Petrenko AG, Geppert M, Sudhof TC. Neurexins: synaptic cell surface proteins related to the alpha-latrotoxin receptor and laminin. Science. 1992;257:50–56. - PubMed
-
- Ushkaryov YA, Hata Y, Ichtchenko K, Moomaw C, Afendis S, et al. Conserved domain structure of beta-neurexins. Unusual cleaved signal sequences in receptor-like neuronal cell-surface proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:11987–11992. - PubMed
-
- Missler M, Sudhof TC. Neurexins: three genes and 1001 products. Trends Genet. 1998;14:20–26. - PubMed
-
- Ullrich B, Ushkaryov YA, Sudhof TC. Cartography of neurexins: more than 1000 isoforms generated by alternative splicing and expressed in distinct subsets of neurons. Neuron. 1995;14:497–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

