Oral muscle relaxant may induce immediate allergic reactions
- PMID: 22665359
- PMCID: PMC3381482
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.4.863
Oral muscle relaxant may induce immediate allergic reactions
Abstract
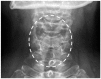
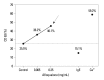
Eperisone and afloqualone act by relaxing both skeletal and vascular smooth muscles to improve circulation and suppress pain reflex. These drugs are typically prescribed with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) as painkillers. However, there have been no reports on serious adverse reactions to oral muscle relaxants; and this is the first report to describe three allergic reactions caused by eperisone and afloqualone. All three patients had histories of allergic reactions after oral intake of multiple painkillers, including oral muscle relaxants and NSAIDs, for chronic muscle pain. An open-label oral challenge test was performed with each drug to confirm which drugs caused the systemic reactions. All patients experienced the same reactions within one hour after oral intake of eperisone or afloqualone. The severity of these reactions ranged from laryngeal edema to hypotension. To confirm that the systemic reaction was caused by eperisone or afloqualone, skin prick testing and intradermal skin tests were performed with eperisone or afloqualone extract in vivo, and basophil activity tests were performed after stimulation with these drugs in vitro. In one patient with laryngeal edema, the intradermal test with afloqualone extract had a positive result, and CD63 expression levels on basophils increased in a dose-dependent manner by stimulation with afloqualone. We report three allergic reactions caused by oral muscle relaxants that might be mediated by non-immunoglobulin E-mediated responses. Since oral muscle relaxants such as eperisone and afloqualone are commonly prescribed for chronic muscle pain and can induce severe allergic reactions, we should prescribe them carefully.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Matsunaga M, Uemura Y, Yonemoto Y, Kanai K, Etoh H, Tanaka S, et al. Long-lasting muscle relaxant activity of eperisone hydrochloride after percutaneous administration in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1997;73:215–220. - PubMed
-
- Ochiai T, Ishida R. Pharmacological studies on 6-amino-2-fluoromethyl-3-(O-tolyl)-4(3H)-quinazolinone (afloqualone), a new centrally acting muscle relaxant. (II) Effects on the spinal reflex potential and the rigidity. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1982;32:427–438. - PubMed
-
- Inoue S, Bian K, Okamura T, Okunishi H, Toda N. Mechanisms of action of eperisone on isolated dog saphenous arteries and veins. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1989;50:271–282. - PubMed
-
- Iwase S, Mano T, Saito M, Ishida G. Effect of a centrally-acting muscle relaxant, eperisone hydrochloride, on muscle sympathetic nerve activity in humans. Funct Neurol. 1992;7:459–470. - PubMed
-
- Choonhakarn C. Non-pigmenting fixed drug eruption: a new case due to eperisone hydrochloride. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:1288–1289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

