Structural basis for WDR5 interaction (Win) motif recognition in human SET1 family histone methyltransferases
- PMID: 22665483
- PMCID: PMC3431640
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.364125
Structural basis for WDR5 interaction (Win) motif recognition in human SET1 family histone methyltransferases
Abstract
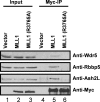
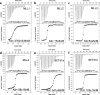
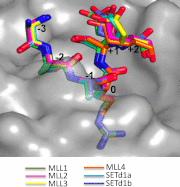
Translocations and amplifications of the mixed lineage leukemia-1 (MLL1) gene are associated with aggressive myeloid and lymphocytic leukemias in humans. MLL1 is a member of the SET1 family of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferases, which are required for transcription of genes involved in hematopoiesis and development. MLL1 associates with a subcomplex containing WDR5, RbBP5, Ash2L, and DPY-30 (WRAD), which together form the MLL1 core complex that is required for sequential mono- and dimethylation of H3K4. We previously demonstrated that WDR5 binds the conserved WDR5 interaction (Win) motif of MLL1 in vitro, an interaction that is required for the H3K4 dimethylation activity of the MLL1 core complex. In this investigation, we demonstrate that arginine 3765 of the MLL1 Win motif is required to co-immunoprecipitate WRAD from mammalian cells, suggesting that the WDR5-Win motif interaction is important for the assembly of the MLL1 core complex in vivo. We also demonstrate that peptides that mimic SET1 family Win motif sequences inhibit H3K4 dimethylation by the MLL1 core complex with varying degrees of efficiency. To understand the structural basis for these differences, we determined structures of WDR5 bound to six different naturally occurring Win motif sequences at resolutions ranging from 1.9 to 1.2 Å. Our results reveal that binding energy differences result from interactions between non-conserved residues C-terminal to the Win motif and to a lesser extent from subtle variation of residues within the Win motif. These results highlight a new class of methylation inhibitors that may be useful for the treatment of MLL1-related malignancies.
Figures




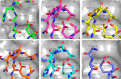

Similar articles
-
Targeted Disruption of the Interaction between WD-40 Repeat Protein 5 (WDR5) and Mixed Lineage Leukemia (MLL)/SET1 Family Proteins Specifically Inhibits MLL1 and SETd1A Methyltransferase Complexes.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 21;291(43):22357-22372. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.752626. Epub 2016 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27563068 Free PMC article.
-
On the mechanism of multiple lysine methylation by the human mixed lineage leukemia protein-1 (MLL1) core complex.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24242-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014498. Epub 2009 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19556245 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical reconstitution and phylogenetic comparison of human SET1 family core complexes involved in histone methylation.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 6;290(10):6361-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.627646. Epub 2015 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25561738 Free PMC article.
-
The Development of Inhibitors Targeting the Mixed Lineage Leukemia 1 (MLL1)-WD Repeat Domain 5 Protein (WDR5) Protein- Protein Interaction.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(33):5530-5542. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190528080514. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31132972 Review.
-
WRAD: enabler of the SET1-family of H3K4 methyltransferases.Brief Funct Genomics. 2012 May;11(3):217-26. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/els017. Epub 2012 May 30. Brief Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22652693 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis of arginine asymmetrical dimethylation by PRMT6.Biochem J. 2016 Oct 1;473(19):3049-63. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160537. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27480107 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of Protein Methyltransferases and Demethylases.Chem Rev. 2018 Feb 14;118(3):989-1068. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00801. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 28338320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse roles of WDR5-RbBP5-ASH2L-DPY30 (WRAD) complex in the functions of the SET1 histone methyltransferase family.J Biosci. 2017 Mar;42(1):155-159. doi: 10.1007/s12038-017-9666-9. J Biosci. 2017. PMID: 28229975 Review.
-
Chemically induced degradation of epigenetic targets.Chem Soc Rev. 2023 Jul 3;52(13):4313-4342. doi: 10.1039/d3cs00100h. Chem Soc Rev. 2023. PMID: 37314393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of Potent and Selective WDR5 Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras as Potential Therapeutics for Pancreatic Cancer.J Med Chem. 2023 Dec 14;66(23):16168-16186. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01521. Epub 2023 Nov 29. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 38019706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cosgrove M. S. (2006) PHinDing a new histone “effector” domain. Structure 14, 1096–1098 - PubMed
-
- Flanagan J. F., Mi L. Z., Chruszcz M., Cymborowski M., Clines K. L., Kim Y., Minor W., Rastinejad F., Khorasanizadeh S. (2005) Double chromodomains cooperate to recognize the methylated histone H3 tail. Nature 438, 1181–1185 - PubMed
-
- Pray-Grant M. G., Daniel J. A., Schieltz D., Yates J. R., 3rd, Grant P. A. (2005) Chd1 chromodomain links histone H3 methylation with SAGA- and SLIK-dependent acetylation. Nature 433, 434–438 - PubMed
-
- Santos-Rosa H., Schneider R., Bernstein B. E., Karabetsou N., Morillon A., Weise C., Schreiber S. L., Mellor J., Kouzarides T. (2003) Methylation of histone H3 K4 mediates association of the Isw1p ATPase with chromatin. Mol. Cell 12, 1325–1332 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

