Molecular characteristics of Clostridium perfringens TpeL toxin and consequences of mono-O-GlcNAcylation of Ras in living cells
- PMID: 22665487
- PMCID: PMC3408161
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.347773
Molecular characteristics of Clostridium perfringens TpeL toxin and consequences of mono-O-GlcNAcylation of Ras in living cells
Abstract
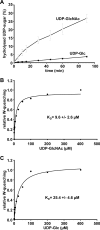
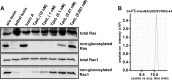
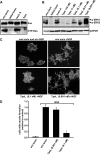
TpeL is a member of the family of clostridial glucosylating toxins produced by Clostridium perfringens type A, B, and C strains. In contrast to other members of this toxin family, it lacks a C-terminal polypeptide repeat domain, which is suggested to be involved in target cell binding. It was shown that the glucosyltransferase domain of TpeL modifies Ras in vitro by mono-O-glucosylation or mono-O-GlcNAcylation (Nagahama, M., Ohkubo, A., Oda, M., Kobayashi, K., Amimoto, K., Miyamoto, K., and Sakurai, J. (2011) Infect. Immun. 79, 905-910). Here we show that TpeL preferably utilizes UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) as a sugar donor. Change of alanine 383 of TpeL to isoleucine turns the sugar donor preference from UDP-GlcNAc to UDP-glucose. In contrast to previous studies, we show that Rac is a poor substrate in vitro and in vivo and requires 1-2 magnitudes higher toxin concentrations for modification by TpeL. The toxin is autoproteolytically processed in the presence of inositol hexakisphosphate (InsP(6)) by an intrinsic cysteine protease domain, located next to the glucosyltransferase domain. A C-terminally extended TpeL full-length variant (TpeL1-1779) induces apoptosis in HeLa cells (most likely by mono-O-GlcNAcylation of Ras), and inhibits Ras signaling including Ras-Raf interaction and ERK activation. In addition, TpeL blocks Ras signaling in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. TpeL is a glucosylating toxin, which modifies Ras and induces apoptosis in target cells without having a typical C-terminal polypeptide repeat domain.
Figures



References
-
- Borriello S. P., Aktories K. (2005) in Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium difficile, and other Clostridium species, Topley Wilson's Microbiology & Microbial Infections (Borriello S. P., Murray P. R., Funke G., eds) Hodder Arnold, London
-
- Smedley J. G., 3rd, Fisher D. J., Sayeed S., Chakrabarti G., McClane B. A. (2004) The enteric toxins of Clostridium perfringens. Rev. Physiol Biochem. Pharmacol. 152, 183–204 - PubMed
-
- Rood J. I. (1998) Virulence genes of Clostridium perfringens. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 52, 333–360 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

