RpaB, another response regulator operating circadian clock-dependent transcriptional regulation in Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942
- PMID: 22665493
- PMCID: PMC3406716
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.338251
RpaB, another response regulator operating circadian clock-dependent transcriptional regulation in Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942
Abstract
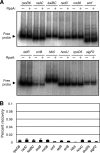
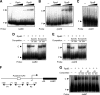
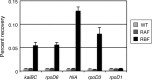
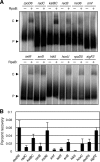
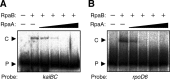
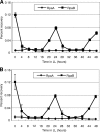
The circadian clock of cyanobacteria is composed of KaiA, KaiB, and KaiC proteins, and the SasA-RpaA two-component system has been implicated in the regulation of one of the output pathways of the clock. In this study, we show that another response regulator that is essential for viability, the RpaA paralog, RpaB, plays a central role in the transcriptional oscillation of clock-regulated genes. In vivo and in vitro analyses revealed that RpaB and not RpaA could specifically bind to the kaiBC promoter, possibly repressing transcription during subjective night. This suggested that binding may be terminated by RpaA to activate gene transcription during subjective day. Moreover, we found that rpoD6 and sigF2, which encode group-2 and group-3 σ factors for RNA polymerase, respectively, were also targets of the RpaAB system, suggesting that a specific group of σ factors can propagate genome-wide transcriptional oscillation. Our findings thus reveal a novel mechanism for a circadian output pathway that is mediated by two paralogous response regulators.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of the Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 homolog of the circadian clock output regulator RpaA in day-night transitions.Mol Microbiol. 2018 Dec;110(5):847-861. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14129. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Mol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30216574
-
An RpaA-Dependent Sigma Factor Cascade Sets the Timing of Circadian Transcriptional Rhythms in Synechococcus elongatus.Cell Rep. 2018 Dec 11;25(11):2937-2945.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.11.049. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30540929
-
A KaiC-associating SasA-RpaA two-component regulatory system as a major circadian timing mediator in cyanobacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 8;103(32):12109-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602955103. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16882723 Free PMC article.
-
The Kai-Protein Clock-Keeping Track of Cyanobacteria's Daily Life.Subcell Biochem. 2019;93:359-391. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-28151-9_12. Subcell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31939158 Review.
-
A cyanobacterial circadian clock based on the Kai oscillator.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:47-55. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2007.72.029. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007. PMID: 18419262 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in primary metabolism under light and dark conditions in response to overproduction of a response regulator RpaA in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Front Microbiol. 2015 Aug 26;6:888. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00888. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26379657 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing a two-loop transcriptional feedback mechanism in the cyanobacterial circadian clock.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(3):e1002966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002966. Epub 2013 Mar 14. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23516349 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk and regulatory interactions between the essential response regulator RpaB and cyanobacterial circadian clock output.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 17;112(7):2198-203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424632112. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25653337 Free PMC article.
-
CryoEM and molecular dynamics of the circadian KaiB-KaiC complex indicates that KaiB monomers interact with KaiC and block ATP binding clefts.J Mol Biol. 2013 Sep 23;425(18):3311-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.06.018. Epub 2013 Jun 22. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23796516 Free PMC article.
-
The human gut and groundwater harbor non-photosynthetic bacteria belonging to a new candidate phylum sibling to Cyanobacteria.Elife. 2013 Oct 1;2:e01102. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01102. Elife. 2013. PMID: 24137540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Young M. W., Kay S. A. (2001) Time zones: a comparative genetics of circadian clocks. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2, 702–715 - PubMed
-
- Ishiura M., Kutsuna S., Aoki S., Iwasaki H., Andersson C. R., Tanabe A., Golden S. S., Johnson C. H., Kondo T. (1998) Expression of a gene cluster kaiABC as a circadian feedback process in cyanobacteria. Science 281, 1519–1523 - PubMed
-
- Kageyama H., Kondo T., Iwasaki H. (2003) Circadian formation of clock protein complexes by KaiA, KaiB, KaiC, and SasA in cyanobacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 2388–2395 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

