The stress response mediator ATF3 represses androgen signaling by binding the androgen receptor
- PMID: 22665497
- PMCID: PMC3434546
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00159-12
The stress response mediator ATF3 represses androgen signaling by binding the androgen receptor
Abstract
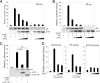
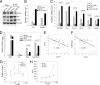
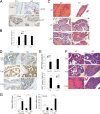
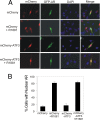
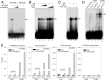
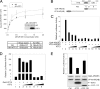
Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) is a common mediator of cellular stress response signaling and is often aberrantly expressed in prostate cancer. We report here that ATF3 can directly bind the androgen receptor (AR) and consequently repress AR-mediated gene expression. The ATF3-AR interaction requires the leucine zipper domain of ATF3 that independently binds the DNA-binding and ligand-binding domains of AR, and the interaction prevents AR from binding to cis-acting elements required for expression of androgen-dependent genes while inhibiting the AR N- and C-terminal interaction. The functional consequences of the loss of ATF3 expression include increased transcription of androgen-dependent genes in prostate cancer cells that correlates with increased ability to grow in low-androgen-containing medium and increased proliferative activity of the prostate epithelium in ATF3 knockout mice that is associated with prostatic hyperplasia. Our results thus demonstrate that ATF3 is a novel repressor of androgen signaling that can inhibit AR functions, allowing prostate cells to restore homeostasis and maintain integrity in the face of a broad spectrum of intrinsic and environmental insults.
Figures


References
-
- Adachi M, et al. 2000. Androgen-insensitivity syndrome as a possible coactivator disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 343:856–862 - PubMed
-
- Andersen R, et al. 2010. Regression of castrate-recurrent prostate cancer by a small-molecule inhibitor of the amino-terminus domain of the androgen receptor. Cancer Cell 17:535–546 - PubMed
-
- Beleza-Meireles A, et al. 2008. Activating transcription 3: a hormone responsive gene in the etiology of hypospadias. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 158:729–739 - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann AO. 2001. Molecular basis of androgen insensitivity. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 179:105–109 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
