Extra-large letter spacing improves reading in dyslexia
- PMID: 22665803
- PMCID: PMC3396504
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1205566109
Extra-large letter spacing improves reading in dyslexia
Abstract
Although the causes of dyslexia are still debated, all researchers agree that the main challenge is to find ways that allow a child with dyslexia to read more words in less time, because reading more is undisputedly the most efficient intervention for dyslexia. Sophisticated training programs exist, but they typically target the component skills of reading, such as phonological awareness. After the component skills have improved, the main challenge remains (that is, reading deficits must be treated by reading more--a vicious circle for a dyslexic child). Here, we show that a simple manipulation of letter spacing substantially improved text reading performance on the fly (without any training) in a large, unselected sample of Italian and French dyslexic children. Extra-large letter spacing helps reading, because dyslexics are abnormally affected by crowding, a perceptual phenomenon with detrimental effects on letter recognition that is modulated by the spacing between letters. Extra-large letter spacing may help to break the vicious circle by rendering the reading material more easily accessible.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


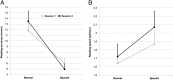
Comment in
-
Helping dyslexic children attend to letters within visual word forms.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 10;109(28):11064-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209921109. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22753488 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Interletter spacing and dyslexia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 30;109(44):E2958; author reply E2959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1212877109. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22961254 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Snowling MJ. Dyslexia. Oxford: Blackwell; 2000.
-
- Shaywitz S. Overcoming Dyslexia. New York: Vintage Books; 2003.
-
- Gabrieli JDE. Dyslexia: A new synergy between education and cognitive neuroscience. Science. 2009;325:280–283. - PubMed
-
- Ramus F. Developmental dyslexia: Specific phonological deficit or general sensorimotor dysfunction? Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:212–218. - PubMed
-
- Tallal P. Improving language and literacy is a matter of time. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:721–728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

