Acute care for elders units produced shorter hospital stays at lower cost while maintaining patients' functional status
- PMID: 22665834
- PMCID: PMC3870859
- DOI: 10.1377/hlthaff.2012.0142
Acute care for elders units produced shorter hospital stays at lower cost while maintaining patients' functional status
Abstract
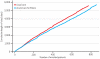
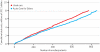
Acute Care for Elders Units offer enhanced care for older adults in specially designed hospital units. The care is delivered by interdisciplinary teams, which can include geriatricians, advanced practice nurses, social workers, pharmacists, and physical therapists. In a randomized controlled trial of 1,632 elderly patients, length-of-stay was significantly shorter-6.7 days per patient versus 7.3 days per patient-among those receiving care in the Acute Care for Elders Unit compared to usual care. This difference produced lower total inpatient costs-$9,477 per patient versus $10,451 per patient-while maintaining patients' functional abilities and not increasing hospital readmission rates. The practices of Acute Care for Elders Units, and the principles they embody, can provide hospitals with effective strategies for lowering costs while preserving quality of care for hospitalized elders.
Figures
References
-
- Creditor MC. Hazards of hospitalization of the elderly. Ann Intern Med. 1993;118(3):219–23. - PubMed
-
- Covinsky KE, Pierluissi E, Johnston CB. Hospitalization-associated disability: “she was probably able to ambulate, but I’m not sure.”. JAMA. 2011;306(16):1782–93. - PubMed
-
- Palmer RM, Landefeld CS, Kresevic D, Kowal J. A medical unit for the acute care of the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994;42(5):545–52. - PubMed
-
- Rubenstein LZ, Stuck AE, Siu AL, Wieland D. Impacts of geriatric evaluation and management programs on defined outcomes: overview of the evidence. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991;39(9 Pt 2):8S–16S. - PubMed
-
- Stuck AE, Siu AL, Wieland GD, Adams J, Rubenstein LZ. Comprehensive geriatric assessment: a meta-analysis of controlled trials. Lancet. 1993;342(8878):1032–6. - PubMed

