Effect of rehabilitation on a patient suffering from a tuberculous brain abscess with Gerstmann's syndrome: case report
- PMID: 22665998
- PMCID: PMC3363139
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S31713
Effect of rehabilitation on a patient suffering from a tuberculous brain abscess with Gerstmann's syndrome: case report
Abstract
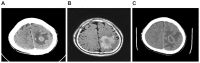
There are few reports in the literature of tuberculous brain abscess. Tuberculous brain abscess usually occurs in an immunocompromised host. Almost all previously documented cases have involved acquired immune deficiency syndrome. We encountered a 53-year-old right-handed immunocompetent male who was initially suspected of having a cerebrovascular accident due to acute-onset right hemiparesis and paresthesia. A tentative diagnosis of brain tumor versus brain abscess was made on imaging studies. The patient was finally diagnosed with a tuberculous brain abscess based upon deterioration on imaging and a positive tuberculosis culture. The tuberculous brain abscess was located in the left parietal lobe, which resulted in Gerstmann's syndrome and right-sided apraxia. Stereotactic surgery was performed. He was also given antituberculosis chemotherapy and comprehensive rehabilitation. Considerable improvement was noted after rehabilitation. The patient even returned to a normal life and work. Our case demonstrates that an aggressive intensive inpatient rehabilitation program combined with stereotactic surgery and effective antituberculosis therapy play an important role in improving the outcome for patients with tuberculous brain abscess, Gerstmann's syndrome, and right-sided apraxia.
Keywords: Gerstmann’s syndrome; rehabilitation; tuberculous brain abscess.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Eclamptogenic Gerstmann's syndrome in combination with cortical agnosia and cortical diplopia.Ger J Ophthalmol. 1995 Jul;4(4):234-8. Ger J Ophthalmol. 1995. PMID: 7492936
-
Acute parietal lobe infarction presenting as Gerstmann's syndrome and cognitive decline mimicking senile dementia.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2013;9:937-40. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S43527. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2013. PMID: 23847420 Free PMC article.
-
White matter tract disconnection in Gerstmann's syndrome: Insights from a single case study.Cortex. 2023 Sep;166:322-337. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2023.05.016. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Cortex. 2023. PMID: 37478549
-
What ever happened to developmental Gerstmann's syndrome? Links to other pediatric, genetic, and neurodevelopmental syndromes.J Child Neurol. 2004 Apr;19(4):282-9. doi: 10.1177/088307380401900408. J Child Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15163095 Review.
-
A proposed reinterpretation of Gerstmann's syndrome.Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2014 Dec;29(8):828-33. doi: 10.1093/arclin/acu056. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2014. PMID: 25377466 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of early rehabilitation therapy on movement ability of hemiplegic lower extremity in patients with acute cerebrovascular accident.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jan;97(2):e9544. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009544. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29480843 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gerstmann syndrome as a sequela of a brain abscess in a non-dominant hemisphere: A case report.Surg Neurol Int. 2025 Mar 28;16:107. doi: 10.25259/SNI_52_2025. eCollection 2025. Surg Neurol Int. 2025. PMID: 40206738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frieden TR, Sterling TR, Munsiff SS, et al. Tuberculosis. Lancet. 2003;362(9387):887–899. - PubMed
-
- Oncul O, Baylan O, Mutlu H, et al. Tuberculous meningitis with multiple intracranial tuberculomas mimicking neurocysticercosis clinical and radiological findings. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2005;58(6):387–389. - PubMed
-
- Farrar DJ, Flanigan TP, Gordon NM, et al. Tuberculous brain abscess in a patient with HIV infection: case report and review. Am J Med. 1997;102(3):297–301. - PubMed
-
- Velasco-Martínez JJ, Guerrero-Espejo A, Gómez-Mampaso E, et al. Tuberculous brain abscess should be considered in HIV/AIDS patients. AIDS. 1995;9(10):1197–1199. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

