Quorum quenching revisited--from signal decays to signalling confusion
- PMID: 22666051
- PMCID: PMC3355433
- DOI: 10.3390/s120404661
Quorum quenching revisited--from signal decays to signalling confusion
Abstract
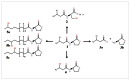
In a polymicrobial community, while some bacteria are communicating with neighboring cells (quorum sensing), others are interrupting the communication (quorum quenching), thus creating a constant arms race between intercellular communication. In the past decade, numerous quorum quenching enzymes have been found and initially thought to inactivate the signalling molecules. Though this is widely accepted, the actual roles of these quorum quenching enzymes are now being uncovered. Recent evidence extends the role of quorum quenching to detoxification or metabolism of signalling molecules as food and energy source; this includes "signalling confusion", a term coined in this paper to refer to the phenomenon of non-destructive modification of signalling molecules. While quorum quenching has been explored as a novel anti-infective therapy targeting, quorum sensing evidence begins to show the development of resistance against quorum quenching.
Keywords: N-acylhomoserine lactone; acylase; anti-biofouling; anti-infective; aquaculture; lactonase; oxidoreductase; paraoxonase; quorum quenching resistance; quorum sensing; signalling confusion.
Figures
References
-
- Fuqua C., Parsek M.R., Greenberg E.P. Regulation of gene expression by cell-to-cell communication: Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2001;35:439–468. - PubMed
-
- Eberhard A., Burlingame A.L., Eberhard C., Kenyon G.L., Nealson K.H., Oppenheimer N.J. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry. 1981;20:2444–2449. - PubMed
-
- Chen X., Schauder S., Potier N., Van Dorsselaer A., Pelczer I., Bassler B.L., Hughson F.M. Structural identification of a bacterial quorum-sensing signal containing boron. Nature. 2002;415:545–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

