Patients with Schizophrenia Fail to Up-Regulate Task-Positive and Down-Regulate Task-Negative Brain Networks: An fMRI Study Using an ICA Analysis Approach
- PMID: 22666197
- PMCID: PMC3364481
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2012.00149
Patients with Schizophrenia Fail to Up-Regulate Task-Positive and Down-Regulate Task-Negative Brain Networks: An fMRI Study Using an ICA Analysis Approach
Erratum in
- Front Hum Neurosci. 2013;7:231
Abstract
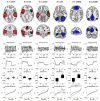
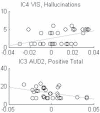
Recent research suggests that the cerebral correlates of cognitive deficits in schizophrenia are nested in the activity of widespread, inter-regional networks rather than being restricted to any specific brain location. One of the networks that have received focus lately is the default mode network. Parts of this network have been reported as hyper-activated in schizophrenia patients (SZ) during rest and during task performance compared to healthy controls (HC), although other parts have been found to be hypo-activated. In contrast to this network, task-positive networks have been reported as hypo-activated compared in SZ during task performance. However, the results are mixed, with, e.g., the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex showing both hyper- and hypo-activation in SZ. In this study we were interested in signal increase and decrease differences between a group of SZ and HC in cortical networks, assuming that the regulatory dynamics of alternating task-positive and task-negative neuronal processes are aberrant in SZ. We compared 31 SZ to age- and gender-matched HC, and used fMRI and independent component analysis (ICA) in order to identify relevant networks. We selected the independent components (ICs) with the largest signal intensity increases (STG, insula, supplementary motor cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, and MTG) and decreases (fusiform gyri, occipital lobe, PFC, cingulate, precuneus, and angular gyrus) in response to a dichotic auditory cognitive task. These ICs were then tested for group differences. Our findings showed deficient up-regulation of the executive network and a corresponding deficit in the down-regulation of the anterior default mode, or effort network during task performance in SZ when compared with HC. These findings may indicate a deficit in the dynamics of alternating task-dependent and task-independent neuronal processes in SZ. The results may cast new light on the mechanisms underlying cognitive deficits in schizophrenia, and may be of relevance for diagnostics and new treatments.
Keywords: ICA; brain activation; cognitive processing; default mode network; dichotic listening; executive network; fMRI; schizophrenia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resting-state hyperconnectivity within the default mode network impedes the ability to initiate cognitive performance in first-episode schizophrenia patients.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Aug 30;102:109959. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.109959. Epub 2020 May 3. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32376341
-
Frontal and superior temporal auditory processing abnormalities in schizophrenia.Neuroimage Clin. 2013 May 15;2:695-702. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.05.002. eCollection 2013. Neuroimage Clin. 2013. PMID: 24179821 Free PMC article.
-
An fMRI investigation of delay discounting in patients with schizophrenia.Brain Behav. 2013 Jul;3(4):384-401. doi: 10.1002/brb3.135. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Brain Behav. 2013. PMID: 24381810 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal default-mode network homogeneity in first-episode, drug-naive schizophrenia at rest.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Mar 3;49:16-20. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.10.021. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24216538
-
[Cognition, schizophrenia and the effect of antipsychotics].Encephale. 2006 May-Jun;32(3 Pt 1):341-50. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(06)76162-0. Encephale. 2006. PMID: 16840928 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Voxel-based versus network-analysis of changes in brain states in patients with auditory verbal hallucinations using the Eriksen Flanker task.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 20;20(3):e0319925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319925. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40112006 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperdeactivation of the Default Mode Network in People With Schizophrenia When Focusing Attention in Space.Schizophr Bull. 2016 Sep;42(5):1158-66. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbw019. Epub 2016 Feb 28. Schizophr Bull. 2016. PMID: 26926831 Free PMC article.
-
The Cannabis Pathway to Non-Affective Psychosis may Reflect Less Neurobiological Vulnerability.Front Psychiatry. 2014 Nov 18;5:159. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00159. eCollection 2014. Front Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25477825 Free PMC article.
-
Shared and distinct brain fMRI response during performance of working memory tasks in adult patients with schizophrenia and major depressive disorder.Hum Brain Mapp. 2021 Nov;42(16):5458-5476. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25618. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021. PMID: 34431584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resting-State EEG Connectivity at High-Frequency Bands and Attentional Performance Dysfunction in Stabilized Schizophrenia Patients.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Apr 9;59(4):737. doi: 10.3390/medicina59040737. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37109695 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

