Oxidative stress, tumor microenvironment, and metabolic reprogramming: a diabolic liaison
- PMID: 22666258
- PMCID: PMC3361160
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/762825
Oxidative stress, tumor microenvironment, and metabolic reprogramming: a diabolic liaison
Abstract
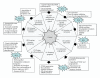
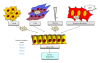
Conversely to normal cells, where deregulated oxidative stress drives the activation of death pathways, malignant cells exploit oxidative milieu for its advantage. Cancer cells are located in a very complex microenvironment together with stromal components that participate to enhance oxidative stress to promote tumor progression. Indeed, convincing experimental and clinical evidence underline the key role of oxidative stress in several tumor aspects thus affecting several characteristics of cancer cells. Oxidants influence the DNA mutational potential, intracellular signaling pathways controlling cell proliferation and survival and cell motility and invasiveness as well as control the reactivity of stromal components that is fundamental for cancer development and dissemination, inflammation, tissue repair, and de novo angiogenesis. This paper is focused on the role of oxidant species in the acquisition of two mandatory features for aggressive neoplastic cells, recently defined by Hanahan and Weinberg as new "hallmarks of cancer": tumor microenvironment and metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells.
Figures
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100(1):57–70. - PubMed
-
- Allen M, Jones JL. Jekyll and hyde: the role of the microenvironment on the progression of cancer. The Journal of Pathology. 2011;223(2):162–176. - PubMed
-
- Landriscina M, Maddalena F, Laudiero G, Esposito F. Adaptation to oxidative stress, chemoresistance, and cell survival. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling. 2009;11(11):2701–2716. - PubMed
-
- Giannoni E, Fiaschi T, Ramponi G, Chiarugi P. Redox regulation of anoikis resistance of metastatic prostate cancer cells: key role for Src and EGFR-mediated pro-survival signals. Oncogene. 2009;28(20):2074–2086. - PubMed
-
- Al Saleh S, Sharaf LH, Luqmani YA. Signalling pathways involved in endocrine resistance in breast cancer and associations with epithelial to mesenchymal transition (review) International Journal of Oncology. 2011;38(5):1197–1217. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

