Multifunctional role of Bcl-2 in malignant transformation and tumorigenesis of Cr(VI)-transformed lung cells
- PMID: 22666341
- PMCID: PMC3362580
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037045
Multifunctional role of Bcl-2 in malignant transformation and tumorigenesis of Cr(VI)-transformed lung cells
Abstract
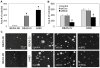
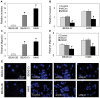
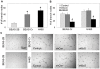
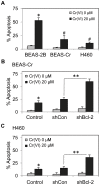
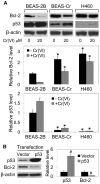
B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) is an antiapoptotic protein known to be important in the regulation of apoptosis in various cell types. However, its role in malignant transformation and tumorigenesis of human lung cells is not well understood. We previously reported that chronic exposure of human lung epithelial cells to the carcinogenic hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) caused malignant transformation and Bcl-2 upregulation; however, the role of Bcl-2 in the transformation is unclear. Using a gene silencing approach, we showed that Bcl-2 plays an important role in the malignant properties of Cr(VI)-transformed cells. Downregulation of Bcl-2 inhibited the invasive and proliferative properties of the cells as well as their colony forming and angiogenic activities, which are upregulated in the transformed cells as compared to control cells. Furthermore, animal studies showed the inhibitory effect of Bcl-2 knockdown on the tumorigenesis of Cr(VI)-transformed cells. The role of Bcl-2 in malignant transformation and tumorigenesis was confirmed by gene silencing experiments using human lung carcinoma NCI-H460 cells. These cells exhibited aggressive malignant phenotypes similar to those of Cr(VI)-transformed cells. Knockdown of Bcl-2 in the H460 cells inhibited malignant and tumorigenic properties of the cells, indicating the general role of Bcl-2 in human lung tumorigenesis. Ingenuity Pathways Analysis (IPA) revealed potential effectors of Bcl-2 in tumorigenesis regulation. Additionally, using IPA together with ectopic expression of p53, we show p53 as an upstream regulator of Bcl-2 in Cr(VI)-transformed cells. Together, our results indicate the novel and multifunctional role of Bcl-2 in malignant transformation and tumorigenesis of human lung epithelial cells chronically exposed to Cr(VI).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Constitutive activation of epidermal growth factor receptor promotes tumorigenesis of Cr(VI)-transformed cells through decreased reactive oxygen species and apoptosis resistance development.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 23;290(4):2213-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.619783. Epub 2014 Dec 4. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25477514 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of hedgehog-interacting protein (HHIP) contributes to hexavalent chromium-induced malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells.Carcinogenesis. 2021 Feb 11;42(1):136-147. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgaa085. Carcinogenesis. 2021. PMID: 32710611 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/p38/Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1α Is Pivotal for Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis of Malignantly Transformed Cells Induced by Hexavalent Chromium.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jul 29;291(31):16271-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.715797. Epub 2016 May 25. J Biol Chem. 2016. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2019 Oct 18;294(42):15558. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RX119.011168. PMID: 27226640 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Assessment of the mode of action for hexavalent chromium-induced lung cancer following inhalation exposures.Toxicology. 2014 Nov 5;325:160-79. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2014.08.009. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Toxicology. 2014. PMID: 25174529 Review.
-
Carcinogenic Mechanisms of Hexavalent Chromium: From DNA Breaks to Chromosome Instability and Neoplastic Transformation.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2024 Dec;11(4):484-546. doi: 10.1007/s40572-024-00460-9. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2024. PMID: 39466546 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of chronic inflammation on Bcl-2 and PCNA expression in prostate needle biopsy specimens.Oncol Lett. 2017 Oct;14(4):3927-3934. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6668. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28943900 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of apoptosis by Bcl-2 cysteine oxidation in human lung epithelial cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Mar;24(6):858-69. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-10-0747. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23363601 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-Induced Apoptosis in Lung Cancer Cells by a Novel Digitoxin Analog.J Cell Physiol. 2016 Apr;231(4):817-28. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25129. J Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26264876 Free PMC article.
-
Pardaxin, a fish antimicrobial peptide, exhibits antitumor activity toward murine fibrosarcoma in vitro and in vivo.Mar Drugs. 2012 Aug;10(8):1852-1872. doi: 10.3390/md10081852. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Mar Drugs. 2012. PMID: 23015777 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA MEG3 in Metal Carcinogenesis.Toxics. 2023 Feb 7;11(2):157. doi: 10.3390/toxics11020157. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 36851033 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberg AJ, Samet JM. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Chest. 2003;124:21S–49S. - PubMed
-
- Machle W, Gregorius F. Cancer of the respiratory system in the United States chromate-producing industry. Public Health Rep. 1948;63:1114–1127. - PubMed
-
- Langard S. One hundred years of chromium and cancer: a review of epidemiological evidence and selected case reports. Am J Ind Med. 1990;17:189–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

