The interplay of neuronal mitochondrial dynamics and bioenergetics: implications for Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 22668779
- PMCID: PMC4015731
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.05.015
The interplay of neuronal mitochondrial dynamics and bioenergetics: implications for Parkinson's disease
Abstract
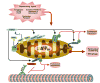
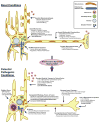
The dynamic properties of mitochondria (mitochondrial fission, fusion, transport biogenesis and degradation) are critical for neuronal function and health, and dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics has been increasingly linked to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD). Mitochondrial dynamics and bioenergetics are interconnected, and this is of particular importance in neurons, which have a unique bioenergetic profile due to their energetic dependence on mitochondria and specialized, compartmentalized energetic needs. In this review, we summarize the interplay of mitochondrial dynamics and bioenergetics, and its particular relevance for neurodegeneration. Evidence linking dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics to PD is presented from both toxin and genetic models, including newly emerging details of how PD-relevant genes PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) and Parkin regulate fission, fusion, mitophagy and transport. Finally, we discuss how neuronal bioenergetics may impact PD-relevant regulation of mitochondrial dynamics, and possible implications for understanding the role of mitochondrial dynamics in PD.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander C, Votruba M, Pesch UE, Thiselton DL, Mayer S, Moore A, Rodriguez M, Kellner U, Leo-Kottler B, Auburger G, Bhattacharya SS, Wissinger B. OPA1, encoding a dynamin-related GTPase, is mutated in autosomal dominant optic atrophy linked to chromosome 3q28. Nat Genet. 2000;26:211–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

