Mathematical simulation of membrane protein clustering for efficient signal transduction
- PMID: 22669501
- PMCID: PMC3822010
- DOI: 10.1007/s10439-012-0599-z
Mathematical simulation of membrane protein clustering for efficient signal transduction
Abstract
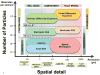
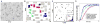
Initiation and propagation of cell signaling depend on productive interactions among signaling proteins at the plasma membrane. These diffusion-limited interactions can be influenced by features of the membrane that introduce barriers, such as cytoskeletal corrals, or microdomains that transiently confine both transmembrane receptors and membrane-tethered peripheral proteins. Membrane topographical features can lead to clustering of receptors and other membrane components, even under very dynamic conditions. This review considers the experimental and mathematical evidence that protein clustering impacts cell signaling in complex ways. Simulation approaches used to consider these stochastic processes are discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Bublil EM, Yarden Y. The EGF receptor family: spearheading a merger of signaling and therapeutics. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19(2):124–34. - PubMed
-
- Keating E, Nohe A, Petersen NO. Studies of distribution, location and dynamic properties of EGFR on the cell surface measured by image correlation spectroscopy. Eur Biophys J. 2008;37(4):469–81. - PubMed
-
- Wennerberg K, Rossman KL, Der CJ. The Ras superfamily at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 5):843–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

