Pulmonary extramedullary haematopoiesis
- PMID: 22669524
- PMCID: PMC3233917
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr.06.2011.4392
Pulmonary extramedullary haematopoiesis
Abstract
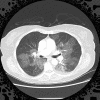
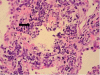
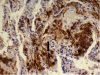
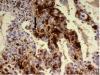
A 72-year-old Caucasian lady with myeloproliferative disorder was admitted for evaluation of progressive dyspnoea, weight loss, fatigue and mild hypoxia. A diffuse ground glass opacity was seen on CT pulmonary angiogram. Differential diagnoses included heart failure, infection, progression of myeloproliferative disorder with extramedullary haematopoiesis, thromboembolism or hydroxyurea-induced lung injury. Bronchoscopy and broncho-alveolar lavage were uninformative however lung biopsy with video-assisted thoracoscopy revealed extramedullary haematopoiesis within lung parenchyma. This is a very rare complication of myeloproliferative disorder and the authors discuss the significance of the case, review the literature and report the patient's progress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Alam R, Padmanabhan K, Rao H. Paravertebral mass in a patient with thalassemia intermedia. Chest 1997;112:265–7 - PubMed
-
- Stein BL, Moliterno AR. Primary myelofibrosis and the myeloproliferative neoplasms: the role of individual variation. JAMA 2010;303:2513–8 - PubMed
-
- Delhommeau F, Dupont S, Della Valle V, et al. Mutation in TET2 in myeloid cancers. N Engl J Med 2009;360:2289–301 - PubMed
-
- Cervantes F, Alvarez-Larrán A, Arellano-Rodrigo E, et al. Frequency and risk factors for thrombosis in idiopathic myelofibrosis: analysis in a series of 155 patients from a single institution. Leukemia 2006;20:55–60 - PubMed
-
- Trow TK, Argento AC, Rubinowitz AN, et al. A 71-year-old woman with myelofibrosis, hypoxemia, and pulmonary hypertension. Chest 2010;138:1506–10 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
