Short-term effectiveness of intravitreal bevacizumab vs. ranibizumab injections for patients with polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
- PMID: 22670070
- PMCID: PMC3364425
- DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2012.26.3.157
Short-term effectiveness of intravitreal bevacizumab vs. ranibizumab injections for patients with polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the effectiveness of intravitreal injections of bevacizumab and ranibizumab in patients with treatment-naive polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV).
Methods: Records from 106 consecutive patients who received intraviteral bevacizumab (n = 58, 1.25 mg) or ranibizumab (n = 52, 0.5 mg) for treatment of PCV were retrospectively reviewed. After three initial monthly loading injections, injection was performed as needed. The main outcome measures included best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), foveal central thickness (FCT) as assessed by spectral domain optical coherence tomography, and the changes in polypoidal lesions based on an indocyanine green angiography.
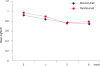
Results: The average number of injections was 3.31 ± 1.25 in the bevacizumab group and 3.44 ± 0.92 in the ranibizumab group. Mean logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution of BCVA from baseline to 6 months after injection improved by 0.17 in the bevacizumab group (p = 0.03) and by 0.19 in the ranibizumab group (p = 0.01). Average FCT decreased from 322 ± 62.48 µm to 274 ± 40.77 µm in the bevacizumab group (p = 0.02) and from 338 ± 50.79 µm to 286 ± 36.93 µm in the ranibizumab group (p = 0.02). Polyp regression rate was 20.7% (12 of 58 eyes) in the bevacizumab group and 21.2% (11 of 52 eyes) in the ranibizumab group. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in BCVA improvement achieved, FCT improvement achieved, and polyp regression rate between groups.
Conclusions: Intravitreal injections of bevacizumab and ranibizumab have similar effects in stabilizing of visual acuity, macular edema, and regression of polypoidal complex in PCV eyes over the short term.
Keywords: Bevacizumab; Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy; Ranibizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Yannuzzi LA, Sorenson J, Spaide RF, Lipson B. Idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (IPCV) Retina. 1990;10:1–82. - PubMed
-
- Yannuzzi LA, Ciardella A, Spaide RF, et al. The expanding clinical spectrum of idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997;115:478–485. - PubMed
-
- Sho K, Takahashi K, Yamada H, et al. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: incidence, demographic features, and clinical characteristics. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121:1392–1396. - PubMed
-
- Spaide RF, Yannuzzi LA, Slakter JS, et al. Indocyanine green videoangiography of idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina. 1995;15:100–110. - PubMed
-
- Chan WM, Lam DS, Lai TY, et al. Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin for symptomatic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: one-year results of a prospective case series. Ophthalmology. 2004;111:1576–1584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources