Induction and exacerbation of psoriasis with Interferon-alpha therapy for hepatitis C: a review and analysis of 36 cases
- PMID: 22671985
- PMCID: PMC3443510
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04582.x
Induction and exacerbation of psoriasis with Interferon-alpha therapy for hepatitis C: a review and analysis of 36 cases
Abstract
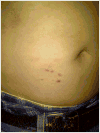
Background: Interferon-alpha (IFN-α) therapy is used to treat hepatitis C infection. The exacerbation and occurrence of psoriasis in hepatitis C patients treated with IFN-α is increasingly recognized, but the distinct associated features, aetiology and management have not been reviewed.
Objective: To review all published cases of hepatitis C patients who developed psoriasis while receiving IFN-α therapy.
Methods: The review was conducted by searching the PubMed database using the keywords 'hepatitis C' AND 'psoriasis.' In addition, references to additional publications not indexed for PubMed were followed to obtain a complete record of published data.
Results: We identified 32 publications describing 36 subjects who developed a psoriatic eruption while receiving IFN-α therapy for hepatitis C. Topical therapies were a commonly employed treatment modality, but led to resolution in only 30% of cases in which they were employed solely. Cessation of IFN-α therapy led to resolution in 93% of cases. Hundred per cent of those who developed psoriasis while on IFN-α therapy responded to systemic therapy and were able to continue the drug.
Conclusion: Further studies and analysis of IFN-α-induced lesions are necessary to clarify the role of IFN-α and the hepatitis C virus in the development of psoriatic lesions.
© 2012 The Authors. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology © 2012 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Edlin B. Five million Americans infected with the hepatitis C virus: a corrected estimate. Hepatology. 2005;42(4 Suppl 1):44.
-
- Armstrong GL, et al. The Prevalence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2006;144(10):705–714. - PubMed
-
- Kim WR. The burden of hepatitis C in the United States. Hepatology. 2002;36(5B):s30–s34. - PubMed
-
- Alberti A, Chemello L, Benvegnù L. Natural history of hepatitis C. Journal of Hepatology. 1999;31 Supplement 1(0):17–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

