The WISTAH hand study: a prospective cohort study of distal upper extremity musculoskeletal disorders
- PMID: 22672216
- PMCID: PMC3476983
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-13-90
The WISTAH hand study: a prospective cohort study of distal upper extremity musculoskeletal disorders
Abstract
Background: Few prospective cohort studies of distal upper extremity musculoskeletal disorders have been performed. Past studies have provided somewhat conflicting evidence for occupational risk factors and have largely reported data without adjustments for many personal and psychosocial factors.
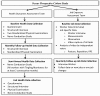
Methods/design: A multi-center prospective cohort study was incepted to quantify risk factors for distal upper extremity musculoskeletal disorders and potentially develop improved methods for analyzing jobs. Disorders to analyze included carpal tunnel syndrome, lateral epicondylalgia, medial epicondylalgia, trigger digit, deQuervain's stenosing tenosynovitis and other tendinoses. Workers have thus far been enrolled from 17 different employment settings in 3 diverse US states and performed widely varying work. At baseline, workers undergo laptop administered questionnaires, structured interviews, two standardized physical examinations and nerve conduction studies to ascertain demographic, medical history, psychosocial factors and current musculoskeletal disorders. All workers' jobs are individually measured for physical factors and are videotaped. Workers are followed monthly for the development of musculoskeletal disorders. Repeat nerve conduction studies are performed for those with symptoms of tingling and numbness in the prior six months. Changes in jobs necessitate re-measure and re-videotaping of job physical factors. Case definitions have been established. Point prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome is a combination of paraesthesias in at least two median nerve-served digits plus an abnormal nerve conduction study at baseline. The lifetime cumulative incidence of carpal tunnel syndrome will also include those with a past history of carpal tunnel syndrome. Incident cases will exclude those with either a past history or prevalent cases at baseline. Statistical methods planned include survival analyses and logistic regression.
Discussion: A prospective cohort study of distal upper extremity musculoskeletal disorders is underway and has successfully enrolled over 1,000 workers to date.
Figures

References
-
- Bureau of Labor Statistics. Workplace Injuries and Illnesses in 2008. Washington, D.C: US Department of Labor; 2011.
-
- Hales TR, Bernard BP. Epidemiology of work-related musculoskeletal disorders. Orthop Clin North Am. 1996;27:679–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

